Zambia
Republic of Zambia
Population
22.02M
Area
752,618 km²
GDP
$26.33B
GDP Per Capita
$3,700
Pop. Density
29/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
ZKZambian kwacha(ZMW)
Calling Code
+260
Timezone
UTC+02:00
Languages
English
Driving Side
left
Demonym
Zambian
Background
Northern Rhodesia’s name was changed to Zambia upon independence from the UK in 1964, under independence leader and first President Kenneth KAUNDA. In the 1980s and 1990s, declining copper prices, economic mismanagement, and a prolonged drought hurt the economy. Elections in 1991 brought an end to one-party rule and propelled the Movement for Multiparty Democracy (MMD) into power. The subsequent vote in 1996, however, saw increasing harassment of opposition parties and abuse of state media and other resources. Administrative problems marked the election in 2001, with three parties filing a legal petition challenging the election of ruling party candidate Levy MWANAWASA. MWANAWASA was reelected in 2006 in an election that was deemed free and fair. Upon his death in 2008, he was succeeded by his vice president, Rupiah BANDA, who won a special presidential byelection later that year. BANDA and the MMD lost to Michael SATA and the Patriotic Front (PF) in the 2011 general elections. SATA, however, presided over a period of haphazard economic management and attempted to silence opposition to PF policies. SATA died in 2014 and was succeeded by his vice president, Guy SCOTT, who served as interim president until 2015, when Edgar LUNGU won the presidential byelection and completed SATA's term. LUNGU then won a full term in the 2016 presidential elections. Hakainde HICHILEMA was elected president in 2021.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑98.3% since 2006Population
↑75.7% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 66.3 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
Geography21
Location
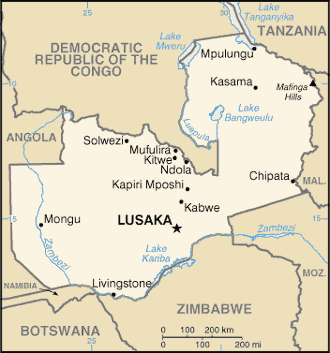
Southern Africa, east of Angola, south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates
15 00 S, 30 00 E
Map references
Africa
Area
land: 743,398 sq km
water: 9,220 sq km
Area - comparative
almost five times the size of Georgia; slightly larger than Texas
Land boundaries
border countries: Angola 1,065 km; Botswana 0.15 km; Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,332 km; Malawi 847 km; Mozambique 439 km; Namibia 244 km; Tanzania 353 km; Zimbabwe 763 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
tropical; modified by altitude; rainy season (October to April)
Terrain
mostly high plateau with some hills and mountains
Elevation
lowest point: Zambezi river 329 m
mean elevation: 1,138 m
Natural resources
copper, cobalt, zinc, lead, coal, emeralds, gold, silver, uranium, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
1,560 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Congo river source (shared with Angola, Republic of Congo, and Democratic Republic of Congo [m]) - 4,700 km; Zambezi river source (shared with Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique [m]) - 2,740 km
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: Zambezi (1,332,412 sq km)
Major aquifers
Upper Kalahari-Cuvelai-Upper Zambezi Basin
Population distribution
one of the highest levels of urbanization in Africa; high density in the central area, particularly around the cities of Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe, and Mufulira, as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
periodic drought; tropical storms (November to April)
Geography - note
landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural river boundary with Zimbabwe; Lake Kariba on the Zambia-Zimbabwe border forms the world's largest reservoir by volume (180 cu km; 43 cu mi)
People & Society34
Population
male: 11,066,079
female: 10,955,892
Nationality
adjective: Zambian
Ethnic groups
Bemba 21%, Tonga 13.6%, Chewa 7.4%, Lozi 5.7%, Nsenga 5.3%, Tumbuka 4.4%, Ngoni 4%, Lala 3.1%, Kaonde 2.9%, Namwanga 2.8%, Lunda (north Western) 2.6%, Mambwe 2.5%, Luvale 2.2%, Lamba 2.1%, Ushi 1.9%, Lenje 1.6%, Bisa 1.6%, Mbunda 1.2%, other 13.8%, unspecified 0.4% (2010 est.)
Languages
Bemba 33.4%, Nyanja 14.7%, Tonga 11.4%, Lozi 5.5%, Chewa 4.5%, Nsenga 2.9%, Tumbuka 2.5%, Lunda (North Western) 1.9%, Kaonde 1.8%, Lala 1.8%, Lamba 1.8%, English (official) 1.7%, Luvale 1.5%, Mambwe 1.3%, Namwanga 1.2%, Lenje 1.1%, Bisa 1%, other 9.7%, unspecified 0.2% (2010 est.)
Religions
Protestant 75.3%, Roman Catholic 20.2%, other 2.7% (includes Muslim, Buddhist, Hindu, and Baha'i), none 1.8% (2010 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 55.1% (male 5,726,265/female 5,736,732)
65 years and over: 2.8% (2024 est.) (male 262,008/female 317,944)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 71.3 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 4.5 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 22.3 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 18.2 years
female: 18.6 years
Population growth rate
2.51% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
29.6 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
4.91 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
0.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
one of the highest levels of urbanization in Africa; high density in the central area, particularly around the cities of Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe, and Mufulira, as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 4.15% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.181 million LUSAKA (capital), 763,000 Kitwe (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.82 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.2 years (2018 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
85 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 38.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 32.1 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 65.2 years
female: 68.7 years
Total fertility rate
3.67 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.81 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 8.9% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.32 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
8.1% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 1.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.36 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 2.16 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 21.4% (2025 est.)
female: 2.4% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
11.8% (2018 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
55.7% (2018 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 29% (2018)
men married by age 18: 2.8% (2018)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 14.5% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 81.7% (2018 est.)
female: 62.2% (2018 est.)
Government23
Country name
conventional short form: Zambia
former: Northern Rhodesia
etymology: name is derived from the Zambezi River, which flows through the western part of the country and forms the southern border with Zimbabwe
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 15 25 S, 28 17 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: named after a village with a headman (chief) called LUSAAKAS
Administrative divisions
10 provinces; Central, Copperbelt, Eastern, Luapula, Lusaka, Muchinga, Northern, North-Western, Southern, Western
Legal system
mixed system of English common law and customary law
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly in two separate readings at least 30 days apart; passage of amendments affecting fundamental rights and freedoms requires approval by at least one half of votes cast in a referendum prior to consideration and voting by the Assembly
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: yes, if at least one parent was a citizen of Zambia
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years for those with an ancestor who was a citizen of Zambia, otherwise 10 years residency is required
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2021: Hakainde HICHILEMA elected president; percent of the vote - Hakainde HICHILEMA (UPND) 57.9%, Edgar LUNGU (PF) 37.3%, other 4.8%
2016: Edgar LUNGU reelected president; percent of vote - Edgar LUNGU (PF) 50.4%, Hakainde HICHILEMA (UPND) 47.6%, other 2%; note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislature name
legislative structure
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president of the republic upon the advice of the 9-member Judicial Service Commission, which is headed by the chief justice, and ratified by the National Assembly; judges normally serve until age 65
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; Industrial Relations Court; subordinate courts (3 levels, based on upper limit of money involved); Small Claims Court; local courts (2 grades, based on upper limit of money involved)
Political parties
Forum for Democracy and Development or FDD
Movement for Multiparty Democracy or MMD
Party of National Unity and Progress or PNUP
Patriotic Front or PF
United Party for National Development or UPND
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 2200 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 234-4009
FAX: [1] (202) 332-0826
email address and website:
[email protected]
https://www.zambiaembassy.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
24 October 1964 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 24 October (1964)
Flag
meaning: green stands for the country's natural resources and vegetation, red for the struggle for freedom, black for the people, and orange for the country's mineral wealth; the eagle represents the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems
National symbol(s)
African fish eagle
National color(s)
green, red, black, orange
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: multiple/Enoch Mankayi SONTONGA
history: adopted 1964; the melody, which comes from the popular song "God Bless Africa," a popular song and anthem in southern Africa
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Mosi-oa-Tunya/Victoria Falls
Economy31
Economic overview
lower-middle-income sub-Saharan economy; regional hydroelectricity producer; trade ties and infrastructure investments from China; IMF assistance to restructure debt burden; one of youngest and fastest-growing labor forces; systemic corruption; extreme rural poverty
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $76.129 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $72.251 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 5.4% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 5.2% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $3,700 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $3,600 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$26.326 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 10.9% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 11% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 37.5% (2024 est.)
services: 55.1% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
sugarcane, cassava, maize, soybeans, milk, vegetables, wheat, groundnuts, sweet potatoes, beef (2023)
Industries
copper mining and processing, emerald mining, construction, foodstuffs, beverages, chemicals, textiles, fertilizer, horticulture
Industrial production growth rate
3.5% (2024 est.)
Labor force
7.407 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 6% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 6% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 10.1% (2024 est.)
female: 9.6% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
60% (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 39.1% (2022 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2022: 0.8% of GDP (2022 est.)
Remittances 2021: 1.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $6.19 billion (2021 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
16.8% (of GDP) (2021 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2022: $1.093 billion (2022 est.)
Current account balance 2021: $2.63 billion (2021 est.)
Exports
Exports 2022: $12.444 billion (2022 est.)
Exports 2021: $11.728 billion (2021 est.)
Exports - partners
Switzerland 27%, China 15%, India 13%, UAE 12%, DRC 10% (2023)
Exports - commodities
raw copper, refined copper, gold, precious stones, electricity (2023)
Imports
Imports 2022: $10.022 billion (2022 est.)
Imports 2021: $7.691 billion (2021 est.)
Imports - partners
South Africa 25%, China 15%, UAE 10%, India 5%, Japan 5% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, fertilizers, trucks, sulphur, tractors (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $2.968 billion (2022 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2021: $2.754 billion (2021 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy6
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 87%
electrification - rural areas: 14.5%
Electricity
consumption: 14.399 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 3 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 180 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.229 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 0.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 87.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
consumption: 2.081 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 15,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 103,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 945 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 109 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
47 state-controlled and private TV stations; state-owned Zambia National Broadcasting Corporation (ZNBC) has 2 TV channels, controls 1, and owns shares in 2 more; 137 radio stations, with 133 private and 4 state-owned (2019)
Internet country code
.zm
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Transportation5
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
9J
Airports
120 (2025)
Heliports
4 (2025)
Railways
narrow gauge: 3,126 km (2014) 1.067-m gauge
Merchant marine
by type: general cargo 1, oil tanker 1
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home Affairs and Internal Security: Zambia Police (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 1.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 1.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 16,000 active Defense Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the ZDF's inventory is largely comprised of Chinese, Russian, and Soviet-era weapons and equipment along with smaller quantities of items from other suppliers such as Israel, South Africa, and the US (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age (17 with parental consent) for voluntary military service for men and women; no conscription; initial service of 7 years followed by 5 in the Reserves (2025)
Military deployments
930 Central African Republic (MINUSCA) (2025)
Military - note
the ZDF traces its roots to the Northern Rhodesia Regiment, which was raised by the British colonial government to fight in World War II; the ZDF was established in 1964 from units of the dissolved Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland armed forces; it participated in a number of regional conflicts during the 1970s and 1980s; Zambia actively supported independence movements such as the Union for the Total Liberation of Angola (UNITA), the Zimbabwe African People's Union (ZAPU), the African National Congress of South Africa (ANC), and the South-West Africa People's Organization (SWAPO) (2025)
Transnational Issues1
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 131,349 (2024 est.)
