United Kingdom
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland; note - the island of Great Britain includes England, Scotland, and Wales
Population
68.75M
Area
243,610 km²
GDP
$3.64T
GDP Per Capita
$52,500
Pop. Density
282/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
£British pound(GBP)
Calling Code
+44
Primary Timezone
UTC-08:00
+8 more
Languages
English
Driving Side
left
Demonym
British
Background
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland was created when the Kingdoms of England and Scotland -- which previously had been distinct states under a single monarchy -- were joined under the 1707 Acts of Union. The island of Ireland was incorporated under the 1800 Acts of Union, while Wales had been part of the Kingdom of England since the 16th century. The United Kingdom has historically played a leading role in developing parliamentary democracy and in advancing literature and science. The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rapid expansion of the British Empire despite the loss of the Thirteen Colonies, and at its zenith in the early 20th century, the British Empire stretched over one fourth of the earth's surface. The first half of the 20th century saw two World Wars seriously deplete the UK's strength and the Irish Republic withdraw from the union. The second half witnessed the dismantling of the Empire and the UK rebuilding itself into a modern and prosperous European nation. As one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council and a founding member of NATO and the Commonwealth of Nations, the UK pursues a global approach to foreign policy. The devolved Scottish Parliament, the National Assembly for Wales, and the Northern Ireland Assembly were established in 1998.
The UK was an active member of the EU after its accession in 1973, although it chose to remain outside the Economic and Monetary Union. However, motivated in part by frustration at a remote bureaucracy in Brussels and massive migration into the country, UK citizens in 2016 voted by 52 to 48 percent to leave the EU. On 31 January 2020, the UK became the only country to depart the EU -- a move known as "Brexit" -- after prolonged negotiations on EU-UK economic and security relationships.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑35.5% since 2006Population
↑13.8% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 81.2 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
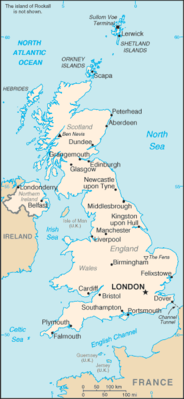
Geography17
Location
Western Europe, islands - including the northern one-sixth of the island of Ireland - between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea; northwest of France
Geographic coordinates
54 00 N, 2 00 W
Map references
Europe
Area
land: 241,930 sq km
water: 1,680 sq km
Area - comparative
twice the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Oregon
Land boundaries
border countries: Ireland 499 km
Coastline
12,429 km
Maritime claims
continental shelf: as defined in continental shelf orders or in accordance with agreed upon boundaries
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Climate
temperate; moderated by prevailing southwest winds over the North Atlantic Current; more than one-half of the days are overcast
Terrain
mostly rugged hills and low mountains; level to rolling plains in east and southeast
Elevation
lowest point: The Fens -4 m
mean elevation: 162 m
Natural resources
coal, petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, lead, zinc, gold, tin, limestone, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, potash, silica sand, slate, arable land
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
718 sq km (2018)
Population distribution
the core of the population lies in and around London, with significant clusters found in central Britain around Manchester and Liverpool, in the Scottish lowlands between Edinburgh and Glasgow, in southern Wales in and around Cardiff, and in far-eastern Northern Ireland, centered on Belfast
Natural hazards
winter windstorms; floods
Geography - note
lies near vital North Atlantic sea lanes; only 35 km (22 mi) from France and linked by tunnel under the English Channel (the Channel Tunnel or Chunnel); because of heavily indented coastline, no location is more than 125 km (78 mi) from tidal waters
People & Society35
Population
male: 34,145,455
female: 34,605,856
Nationality
adjective: British
Ethnic groups
White 87.2%, Black/African/Caribbean/black British 3%, Asian/Asian British: Indian 2.3%, Asian/Asian British: Pakistani 1.9%, mixed 2%, other 3.7% (2011 est.)
Languages
English
Religions
Christian (includes Anglican, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian, Methodist) 59.5%, Muslim 4.4%, Hindu 1.3%, other 2%, unspecified 7.2%, none 25.7% (2011 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 63.9% (male 22,062,643/female 21,702,401)
65 years and over: 19.3% (2024 est.) (male 6,069,865/female 7,158,544)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 26 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 30.7 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 3.3 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 40.1 years
female: 41.5 years
Population growth rate
0.4% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
10.76 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
9.25 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
2.52 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
the core of the population lies in and around London, with significant clusters found in central Britain around Manchester and Liverpool, in the Scottish lowlands between Edinburgh and Glasgow, in southern Wales in and around Cardiff, and in far-eastern Northern Ireland, centered on Belfast
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.8% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
9.648 million LONDON (capital), 2.791 million Manchester, 2.665 million Birmingham, 1.929 million West Yorkshire, 1.698 million Glasgow, 952,000 Southampton/Portsmouth (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
29 years (2018 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
8 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 4.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.3 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 80.1 years
female: 84.4 years
Total fertility rate
1.64 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.8 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 20.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
3.3 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
2.4 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
27.8% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 3.53 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.3 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.35 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.61 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 13.3% (2025 est.)
female: 9.8% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
0.6% (2019 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
49.7% (2021 est.)
Child marriage
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 11.8% national budget (2021 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 17 years (2022 est.)
female: 18 years (2022 est.)
Government26
Country name
conventional short form: United Kingdom
abbreviation: UK
etymology: the name United Kingdom is self-descriptive; the name Britain probably derives from the Celtic word pretani, meaning "painted people;" the designation of Great Britain for England, Scotland, and Wales dates back to medieval times and was used to distinguish the island from Little Britain, or Brittany, in modern France; the name Ireland evolved from the Gaelic name Eriu, which is possibly derived from the Old Celtic iveriu, meaning "good land"
Government type
parliamentary constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
Capital
name
geographic coordinates
time difference
daylight saving time
time zone note
etymology
Administrative divisions
two-tier counties: Cambridgeshire, Cumbria, Derbyshire, Devon, East Sussex, Essex, Gloucestershire, Hampshire, Hertfordshire, Kent, Lancashire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire, Norfolk, North Yorkshire, Nottinghamshire, Oxfordshire, Somerset, Staffordshire, Suffolk, Surrey, Warwickshire, West Sussex, Worcestershire
London boroughs and City of London or Greater London: Barking and Dagenham, Barnet, Bexley, Brent, Bromley, Camden, Croydon, Ealing, Enfield, Greenwich, Hackney, Hammersmith and Fulham, Haringey, Harrow, Havering, Hillingdon, Hounslow, Islington, Kensington and Chelsea, Kingston upon Thames, Lambeth, Lewisham, City of London, Merton, Newham, Redbridge, Richmond upon Thames, Southwark, Sutton, Tower Hamlets, Waltham Forest, Wandsworth, Westminster
metropolitan districts: Barnsley, Birmingham, Bolton, Bradford, Bury, Calderdale, Coventry, Doncaster, Dudley, Gateshead, Kirklees, Knowlsey, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, North Tyneside, Oldham, Rochdale, Rotherham, Salford, Sandwell, Sefton, Sheffield, Solihull, South Tyneside, St. Helens, Stockport, Sunderland, Tameside, Trafford, Wakefield, Walsall, Wigan, Wirral, Wolverhampton
unitary authorities: Bath and North East Somerset; Bedford; Blackburn with Darwen; Blackpool; Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole; Bracknell Forest; Brighton and Hove; City of Bristol; Buckinghamshire; Central Bedfordshire; Cheshire East; Cheshire West and Chester; Cornwall; Darlington; Derby; Dorset; Durham County*; East Riding of Yorkshire; Halton; Hartlepool; Herefordshire*; Isle of Wight*; Isles of Scilly; City of Kingston upon Hull; Leicester; Luton; Medway; Middlesbrough; Milton Keynes; North East Lincolnshire; North Lincolnshire; North Northamptonshire; North Somerset; Northumberland*; Nottingham; Peterborough; Plymouth; Portsmouth; Reading; Redcar and Cleveland; Rutland; Shropshire; Slough; South Gloucestershire; Southampton; Southend-on-Sea; Stockton-on-Tees; Stoke-on-Trent; Swindon; Telford and Wrekin; Thurrock; Torbay; Warrington; West Berkshire; West Northamptonshire; Wiltshire; Windsor and Maidenhead; Wokingham; York
Northern Ireland: 5 borough councils, 4 district councils, 2 city councils
borough councils: Antrim and Newtownabbey; Ards and North Down; Armagh City, Banbridge, and Craigavon; Causeway Coast and Glens; Mid and East Antrim
district councils: Derry City and Strabane; Fermanagh and Omagh; Mid Ulster; Newry, Murne, and Down city councils: Belfast; Lisburn and Castlereagh
Scotland: 32 council areas
council areas: Aberdeen City, Aberdeenshire, Angus, Argyll and Bute, Clackmannanshire, Dumfries and Galloway, Dundee City, East Ayrshire, East Dunbartonshire, East Lothian, East Renfrewshire, City of Edinburgh, Eilean Siar (Western Isles), Falkirk, Fife, Glasgow City, Highland, Inverclyde, Midlothian, Moray, North Ayrshire, North Lanarkshire, Orkney Islands, Perth and Kinross, Renfrewshire, Shetland Islands, South Ayrshire, South Lanarkshire, Stirling, The Scottish Borders, West Dunbartonshire, West Lothian
Wales: 22 unitary authorities
unitary authorities: Blaenau Gwent, Bridgend, Caerphilly, Cardiff, Carmarthenshire, Ceredigion, Conwy, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Isle of Anglesey, Merthyr Tydfil, Monmouthshire, Neath Port Talbot, Newport, Pembrokeshire, Powys, Rhondda Cynon Taff, Swansea, The Vale of Glamorgan, Torfaen, Wrexham
Dependent areas
Anguilla; Bermuda; British Indian Ocean Territory; British Virgin Islands; Cayman Islands; Falkland Islands; Gibraltar; Montserrat; Pitcairn Islands; Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; Turks and Caicos Islands (12)
Legal system
common law system; has nonbinding judicial review of Acts of Parliament under the Human Rights Act of 1998
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as a bill for an Act of Parliament by the government, by the House of Commons, or by the House of Lords; passage requires agreement by both houses and by the monarch (Royal Assent)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the United Kingdom
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Keir STARMER (since 5 July 2024)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister
election/appointment process: the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually becomes the prime minister
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 800 (all appointed)
parties elected and seats per party: Conservative Party (286); Labour Party (212); Liberal Democrats (76); Crossover (Independents) 180; other (6)
percentage of women in chamber: 31%
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: judge candidates selected by an independent committee of several judicial commissions, then recommended to the prime minister, and appointed by the monarch; justices serve for life
subordinate courts: England and Wales: Court of Appeal (civil and criminal divisions); High Court; Crown Court; County Courts; Magistrates' Courts; Scotland: Court of Sessions; Sheriff Courts; High Court of Justiciary; tribunals; Northern Ireland: Court of Appeal in Northern Ireland; High Court; county courts; magistrates' courts; specialized tribunals
Political parties
Conservative and Unionist Party
Democratic Unionist Party or DUP (Northern Ireland)
Green Party of England and Wales or Greens
Labor (Labour) Party
Liberal Democrats (Lib Dems)
Party of Wales (Plaid Cymru)
Reform UK
Scottish National Party or SNP
Sinn Fein (Northern Ireland)
Social Democratic and Labor Party or SDLP (Northern Ireland)
Traditional Unionist Voice or TUV
UK Independence Party or UKIP
Ulster Unionist Party or UUP (Northern Ireland)
Workers Party of Great Britian
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
consulate(s) general
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, C, CBSS (observer), CD, CDB, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), SELEC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNMISS, UNOOSA, UNRWA, UN Security Council (permanent), UNSOM, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Independence
no official date of independence: 927 (minor English kingdoms unite); 3 March 1284 (enactment of the Statute of Rhuddlan uniting England and Wales); 1536 (Act of Union incorporates England and Wales); 1 May 1707 (Acts of Union unite England, Scotland, and Wales as Great Britain); 1 January 1801 (Acts of Union unite Great Britain and Ireland as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland); 6 December 1921 (Anglo-Irish Treaty formalizes partition of Ireland; six counties become Northern Ireland and remain part of the UK); 12 April 1927 (Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act establishes current name of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland)
National holiday
the UK does not celebrate one particular national holiday
Flag
history: the official name is the Union Flag, but commonly called the Union Jack; the design and colors have been the basis for a number of other flags
National symbol(s)
lion (all of Britain); lion, Tudor rose, oak (England); lion, unicorn, thistle (Scotland); dragon, daffodil, leek (Wales); shamrock, flax (Northern Ireland)
National color(s)
red, white, blue (all of Britain); red, white (England); blue, white (Scotland); red, white, green (Wales)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: unknown
history: in use since 1745; by tradition, the song serves as both the national and royal anthem; it is known as either "God Save the Queen" or "God Save the King," depending on the gender of the reigning monarch; it also serves as the royal anthem for many Commonwealth nations
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Giant's Causeway and Causeway Coast (n); Ironbridge Gorge (c); Stonehenge, Avebury, and Associated Sites (c); Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd (c); Blenheim Palace (c); City of Bath (c); Tower of London (c); St Kilda (m); Maritime Greenwich (c); Old and New Towns of Edinburgh (c); Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (c); The English Lake District (c)
Economy31
Economic overview
high-income, non-EU European economy; global financial center and dominant service sector; sluggish growth from stringent monetary policy, reduced business investment, low productivity and participation rates; fiscal austerity in face of high public debt
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $3.596 trillion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $3.582 trillion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 0.4% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 4.8% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $52,500 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $53,000 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$3.644 trillion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 6.8% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 7.9% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 16.7% (2024 est.)
services: 72.8% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, sugar beets, barley, potatoes, chicken, rapeseed, pork, beef, oats (2023)
Industries
machine tools, electric power equipment, automation equipment, railroad equipment, shipbuilding, aircraft, motor vehicles and parts, electronics and communications equipment, metals, chemicals, coal, petroleum, paper and paper products, food processing, textiles, clothing, other consumer goods
Industrial production growth rate
-0.5% (2024 est.)
Labor force
35.359 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 4% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 3.8% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 14.9% (2024 est.)
female: 9.7% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
18.6% (2017 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 3% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 24.6% (2021 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 0.1% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 0.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $1.442 trillion (2023 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
27.4% (of GDP) (2023 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: -$118.354 billion (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: -$70.962 billion (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $1.078 trillion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $1.041 trillion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
USA 14%, China 8%, Germany 8%, Netherlands 7%, Ireland 7% (2023)
Exports - commodities
cars, gold, gas turbines, packaged medicine, crude petroleum (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $1.114 trillion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $1.1 trillion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
China 13%, USA 11%, Germany 10%, France 5%, Norway 4% (2023)
Imports - commodities
cars, gold, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, natural gas (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $177.915 billion (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $176.41 billion (2022 est.)
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy8
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 99.9%
electrification - rural areas: 100%
Electricity
consumption: 262.166 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 9.449 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 33.212 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 28.961 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels
nuclear
solar
wind
hydroelectricity
biomass and waste
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors under construction: 2 (2025)
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 5.88GW (2025 est.)
Percent of total electricity production: 12.5% (2023 est.)
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 36 (2025)
Coal
consumption: 7.372 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 981,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 6.633 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 26 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 1.406 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 2.5 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 63.553 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 15.842 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 45.226 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 180.661 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 39 (2023 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 122 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
public-service British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is the largest broadcasting company in the world; BBC operates multiple TV networks with regional and local TV; mixed system of public and commercial TV broadcasters along with satellite and cable systems provide access to hundreds of international TV stations; BBC operates multiple national, regional, and local radio networks with multiple transmission sites; large number of commercial and satellite radio stations available (2018)
Internet country code
.uk
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 41 (2023 est.)
Transportation7
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
G
Airports
1,057 (2025)
Heliports
139 (2025)
Railways
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 34, container ship 46, general cargo 62, oil tanker 13, other 713
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
size unknown
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Transportation - note
begun in 1988 and completed in 1994, the Channel Tunnel (nicknamed the Chunnel) is a 50.5-km (31.4-mi) rail tunnel under the English Channel at the Strait of Dover; it runs from Folkestone, Kent, in England to Coquelles, Pas-de-Calais, in northern France and is the only fixed link between the island of Great Britain and mainland Europe
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
United Kingdom Armed Forces (aka British Armed Forces, aka His Majesty's Armed Forces): British Army, Royal Navy (includes Royal Marines), Royal Air Force (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2024: 2.3% of GDP (2024 est.)
Military Expenditures 2023: 2.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 2.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 2.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 138,000 Regular Forces (75,000 Army including the Gurkhas; 32,000 Navy including the Royal Marines; 31,000 Air Force) (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the British military's inventory is comprised of domestically produced armaments and imported Western weapons systems, particularly from the US; the UK defense industry is capable of producing air, land, and sea weapons systems and is one of the world's top weapons suppliers; it also cooperates with other European countries, as well as Australia and the US, in the research and development of weapons systems (2025)
Military service age and obligation
16 years of age for enlisted ranks (with parental consent for under 18) and 18 years of age for officers; maximum age varies by military service; conscription abolished in 1963 (2026)
Military deployments
the British military has more than 8,000 personnel on permanent or long-term rotational deployments around the globe in support of NATO, UN, or other commitments and agreements; key deployments include approximately 1,000 in Brunei, approximately 2,500 in Cyprus (includes 250 for UNFICYP), approximately 900-1,000 in Estonia (NATO), over 1,000 in the Falkland Islands, 500-600 in Gibraltar, and more than 1,000 in the Middle East; its air and naval forces conduct missions on a global basis; the British military also participates in large scale NATO exercises, including providing some 16,000 personnel for the 6-month 2024 Steadfast Defender exercise (2024)
Military - note
the UK is a member of the Five Power Defense Arrangements (FPDA), a series of mutual assistance agreements reached in 1971 embracing Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the UK; in 2014, the UK led the formation of the Joint Expeditionary Force (JEF), a pool of high-readiness military forces from the Baltic and Scandinavian countries intended to respond to a wide range of contingencies both in peacetime and in times of crisis or conflict; the UK military also has strong bilateral ties with a variety of foreign militaries, particularly the US, with which it has a mutual defense treaty; British and US military forces have routinely operated side-by-side across a wide range of operations; other close military relationships include Australia, France, Germany, and the Netherlands; in 2010, for example, France and the UK signed a declaration on defense and security cooperation that included greater military interoperability and a Combined Joint Expeditionary Force (CJEF), a deployable, combined Anglo-French military force for use in a range of crisis scenarios (2025)
Transnational Issues2
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 4,672 (2024 est.)
Illicit drugs
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
Compare United Kingdom
See how United Kingdom compares to other countries side by side.
Compare Countries