Timor-Leste
Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste
Population
1.40M
Area
14,874 km²
GDP
$1.88B
GDP Per Capita
$4,200
Pop. Density
94/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
$United States dollar(USD)
Calling Code
+670
Timezone
UTC+09:00
Languages
Portuguese, Tetum
Driving Side
left
Demonym
East Timorese
Background
The island of Timor was actively involved in Southeast Asian trading networks for centuries, and by the 14th century, it exported sandalwood, slaves, honey, and wax. The sandalwood trade attracted the Portuguese, who arrived in the early 16th century; by mid-century, they had colonized the island, which was previously ruled by local chieftains. In 1859, Portugal ceded the western portion of the island to the Dutch. Imperial Japan occupied Portuguese Timor from 1942 to 1945, but Portugal resumed colonial authority after the Japanese defeat in World War II. The eastern part of Timor declared itself independent from Portugal on 28 November 1975, but Indonesian forces invaded and occupied the area nine days later. It was incorporated into Indonesia in 1976 as the province of Timor Timur (East Timor or Timor Leste). Indonesia conducted an unsuccessful pacification campaign in the province over the next two decades, during which as many as 250,000 people died.
In a UN-supervised referendum in 1999, an overwhelming majority of the people of Timor-Leste voted for independence from Indonesia. However, anti-independence Timorese militias -- organized and supported by the Indonesian military -- began a large-scale, scorched-earth campaign of retribution, killing approximately 1,400 Timorese and displacing nearly 500,000. Most of the country's infrastructure was destroyed, including homes, irrigation systems, water supply systems, schools, and most of the electrical grid. Australian-led peacekeeping troops eventually deployed to the country and ended the violence. In 2002, Timor-Leste was internationally recognized as an independent state.
In 2006, Australia and the UN had to step in again to stabilize the country, which allowed presidential and parliamentary elections to be conducted in 2007 in a largely peaceful atmosphere. In 2008, rebels staged an unsuccessful attack against the president and prime minister. Since that attack, Timor-Leste has made considerable progress in building stability and democratic institutions, holding a series of successful parliamentary and presidential elections since 2012. Nonetheless, weak and unstable political coalitions have led to periodic episodes of stalemate and crisis. The UN continues to provide assistance on economic development and strengthening governing institutions. Currently, Timor-Leste is one of the world's poorest nations, with an economy that relies heavily on energy resources in the Timor Sea.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑311.1% since 2006Population
↑43.4% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 67.7 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
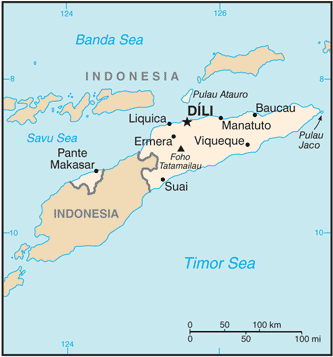
Geography17
Location
Southeastern Asia, northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian archipelago; note - Timor-Leste includes the eastern half of the island of Timor, the Oecussi (Ambeno) region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Pulau Atauro and Pulau Jaco
Geographic coordinates
8 50 S, 125 55 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Area
land: 14,874 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than Connecticut; almost half the size of Maryland
Land boundaries
border countries: Indonesia 253 km
Coastline
706 km
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; hot, humid; distinct rainy and dry seasons
Terrain
mountainous
Elevation
lowest point: Timor Sea, Savu Sea, and Banda Sea 0 m
Natural resources
gold, petroleum, natural gas, manganese, marble
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
350 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
most of the population is concentrated in the western third of the country, particularly around Dili
Natural hazards
floods and landslides are common; earthquakes; tsunamis; tropical cyclones
Geography - note
the island of Timor is part of the Malay Archipelago and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands; the district of Oecussi is an exclave separated from Timor-Leste proper by Indonesia; Timor-Leste is the only Asian country located completely in the Southern Hemisphere
People & Society35
Population
male: 693,940
female: 710,845
Nationality
adjective: Timorese
Ethnic groups
Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) (includes Tetun, Mambai, Tokodede, Galoli, Kemak, Baikeno), Melanesian-Papuan (includes Bunak, Fataluku, Bakasai), small Chinese minority
Languages
Tetun Prasa 30.6%, Mambai 16.6%, Makasai 10.5%, Tetun Terik 6.1%, Baikenu 5.9%, Kemak 5.8%, Bunak 5.5%, Tokodede 4%, Fataluku 3.5%, Waima'a 1.8%, Galoli 1.4%, Naueti 1.4%, Idate 1.2%, Midiki 1.2%, other 4.5% (2015 est.)
Religions
Catholic 90.7%, other 7.1%, Protestant Evangelical 1.9%; less than 1%: Islam, Buddhist, Hindu (2022 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 56.8% (male 418,493/female 437,727)
65 years and over: 4.5% (2024 est.) (male 32,243/female 35,101)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 54.3 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 7.7 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 12.9 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 19.8 years
female: 21.3 years
Population growth rate
1.28% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
23.39 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
6.86 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-3.73 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
most of the population is concentrated in the western third of the country, particularly around Dili
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 3.31% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
281,000 DILI (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.92 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
23 years (2016 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
192 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 35.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 28.9 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 68.9 years
female: 72.3 years
Total fertility rate
2.79 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.35 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 8.9% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.75 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
3.8% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.27 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.09 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 62.6% (2025 est.)
female: 8.9% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
31.9% (2020 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
56.4% (2022 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 14.9% (2016)
men married by age 18: 1.2% (2016)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 4.3% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 73.1% (2022 est.)
female: 71.8% (2022 est.)
People - note
one of only two predominantly Christian nations in Southeast Asia, the other being the Philippines
Government22
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
former
etymology
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 8 35 S, 125 36 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
Legal system
civil law system based on the Portuguese model
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by Parliament and parliamentary groups; consideration of amendments requires at least four-fifths majority approval by Parliament; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by Parliament and promulgation by the president of the republic; passage of amendments to the republican form of government and the flag requires approval in a referendum
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Timor-Leste
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
17 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2022: José RAMOS-HORTA elected president in second round - RAMOS-HORTA (CNRT) 62.1%, Francisco GUTERRES (FRETILIN) 37.9%
2017: Francisco GUTERRES elected president; Francisco GUTERRES (FRETILIN) 57.1%, António da CONCEICAO (PD) 32.5%, other 10.4%
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislature name
legislative structure
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: court president appointed by the president of the republic from among the other court judges to serve a 4-year term; other court judges appointed - 1 by the Parliament and the others by the Supreme Council for the Judiciary, a body chaired by the court president and that includes mostly presidential and parliamentary appointees; other judges serve for life
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Administrative, Tax, and Audit Court; district courts; magistrates' courts; military courts
Political parties
National Congress for Timorese Reconstruction or CNRT
National Unity of the Sons of Timor (Haburas Unidade Nasional Timor Oan or KHUNTO)
People's Liberation Party or PLP
Revolutionary Front of Independent Timor-Leste or FRETILIN
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 4201 Connecticut Avenue NW, Suite 504, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 966-3202
FAX: [1] (202) 966-3205
email address and website:
[email protected]
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, ARF, ASEAN, CPLP, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WMO
Independence
28 November 1975 (from Portugal); 20 May 2002 (from Indonesia)
National holiday
Restoration of Independence Day, 20 May (2002); Proclamation of Independence Day, 28 November (1975)
Flag
meaning: yellow stands for past colonialism, black for obscurantism that needs to be overcome, and red for the struggle for freedom; the white star represents peace and a guiding light
National symbol(s)
Mount Ramelau
National color(s)
red, yellow, black, white
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Fransisco Borja DA COSTA/Afonso DE ARAUJO
history: adopted 2002; the song was first used as an anthem when Timor-Leste declared its independence from Portugal in 1975; the lyricist, Francisco Borja DA COSTA, was killed in the Indonesian invasion just days after independence was declared
Economy28
Economic overview
lower middle-income Southeast Asian economy; government expenditures funded via oil fund drawdowns; endemic corruption undermines growth; foreign aid-dependent; wide-scale poverty, unemployment, and illiteracy
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $5.995 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $7.322 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: -18.1% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: -20.5% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $4,300 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $5,300 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$1.881 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 8.4% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 7% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 23.9% (2023 est.)
services: 61% (2023 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
maize, rice, coconuts, root vegetables, vegetables, cassava, other meats, pork, beans, coffee (2023)
Industries
printing, soap manufacturing, handicrafts, woven cloth
Industrial production growth rate
-57% (2023 est.)
Labor force
615,900 (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 1.6% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 1.6% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 3.2% (2024 est.)
female: 3.7% (2024 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 9.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 5.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $1.826 billion (2022 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
21.6% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: -$177.336 million (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: $408.059 million (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $701.808 million (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $1.858 billion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
China 46%, Singapore 25%, Japan 15%, Indonesia 5%, USA 3% (2023)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, natural gas, coffee, scrap iron, telephones (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $1.169 billion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $1.286 billion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
Indonesia 34%, China 26%, Singapore 9%, Taiwan 5%, India 4% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, rice, cars, plastic products, trucks (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $781.995 million (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $830.81 million (2022 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
the US dollar is used
Energy7
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 100%
Electricity
consumption: 411.519 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 99.481 million kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 5,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
Natural gas
exports: 521.034 million cubic meters (2023 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 116 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
7 TV stations (3 nationwide satellite coverage; 2 terrestrial coverage, mostly in Dili; 2 cable) and 21 radio stations (3 nationwide coverage) (2019)
Internet country code
.tl
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Transportation5
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
4W
Airports
11 (2025)
Heliports
2 (2025)
Merchant marine
by type: other 1
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security6
Military and security forces
Ministry of Interior: National Police of Timor-Leste (Polícia Nacional de Timor-Leste, PNTL) (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 2.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 1.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 2,000 Defense Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military is lightly armed with a limited inventory consisting mostly of donated equipment from countries such as Australia, China, Portugal, South Korea, and the US (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; according to Timorese law on military service, all citizens 18-30 must contribute to the defense of independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of the country and render their contribution through defense and security institutions (2025)
Military - note
the Timor-Leste Defense Force (F-FDTL) has both external defense and internal security roles; it also engages in national development missions, international peacekeeping, and regional security cooperation; the F-FDTL has ties with a variety of partners, including Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Portugal, the UN, and the US (2025)
