North Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Population
26.40M
Area
120,538 km²
GDP
$16.45B
GDP Per Capita
$600
Pop. Density
219/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
₩North Korean won(KPW)
Calling Code
+850
Timezone
UTC+09:00
Languages
Korean
Driving Side
right
Demonym
North Korean
Background
The first recorded kingdom (Choson) on the Korean Peninsula dates from approximately 2300 B.C. Over the subsequent centuries, three main kingdoms -- Kogoryo, Paekche, and Silla -- were established on the Peninsula. By the 5th century A.D., Kogoryo emerged as the most powerful, with control over much of the Peninsula and part of Manchuria (modern-day northeast China). However, Silla allied with the Chinese to create the first unified Korean state in 688. Following the collapse of Silla in the 9th century, Korea was unified under the Koryo (Goryeo; 918-1392) and the Chosen (Joseon; 1392-1910) dynasties. Korea became the object of intense imperialistic rivalry among the Chinese (its traditional benefactor), Japanese, and Russian empires in the latter half of the 19th and early 20th centuries. After the Sino-Japanese War (1894-95) and the Russo-Japanese War (1904-05), Korea was occupied by Imperial Japan. In 1910, Japan formally annexed the entire peninsula. After World War II, the northern half came under Soviet-sponsored communist control.
In 1948, North Korea (formally known as the Democratic People's Republic of Korea or DPRK) was founded under President KIM Il Sung, who consolidated power and cemented autocratic one-party rule under the Korean Worker's Party (KWP). North Korea failed to conquer UN-backed South Korea (formally the Republic of Korea or ROK) during the Korean War (1950-53), after which a demilitarized zone separated the two Koreas. KIM's authoritarian rule included tight control over North Korean citizens and the demonization of the US as the central threat to North Korea's political and social system. In addition, he molded the country's economic, military, and political policies around the core objective of unifying Korea under Pyongyang's control. North Korea also declared a central ideology of juche ("self-reliance") as a check against outside influence, while continuing to rely heavily on China and the Soviet Union for economic support. KIM Il Sung's son, KIM Jong Il, was officially designated as his father's successor in 1980, and he assumed a growing political and managerial role until the elder KIM's death in 1994. Under KIM Jong Il's reign, North Korea continued developing nuclear weapons and ballistic missiles. KIM Jong Un was publicly unveiled as his father's successor in 2010. Following KIM Jong Il's death in 2011, KIM Jong Un quickly assumed power and has since occupied the regime's highest political and military posts.
After the end of Soviet aid in 1991, North Korea faced serious economic setbacks that exacerbated decades of economic mismanagement and resource misallocation. Since the mid-1990s, North Korea has faced chronic food shortages and economic stagnation. In recent years, the North's domestic agricultural production has improved but still falls far short of producing sufficient food for its population. Starting in 2002, North Korea began to tolerate semi-private markets but has made few other efforts to meet its goal of improving the overall standard of living. New economic development plans in the 2010s failed to meet government-mandated goals for key industrial sectors, food production, or overall economic performance. At the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, North Korea instituted a nationwide lockdown that severely restricted its economy and international engagement. Since then, KIM has repeatedly expressed concerns with the regime's economic failures and food problems, but in 2021, he vowed to continue "self-reliant" policies and has reinvigorated his pursuit of greater regime control of the economy.
As of 2024, despite slowly renewing cross-border trade with China, North Korea remained one of the world's most isolated countries and one of Asia's poorest. In 2024, Pyongyang announced it was ending all economic cooperation with South Korea. The move followed earlier proclamations that it was scrapping a 2018 military pact with South Korea to de-escalate tensions along their militarized border, abandoning the country’s decades-long pursuit of peaceful unification with South Korea, and designating the South as North Korea’s “principal enemy.”
Historical Trends
Population
↑8.1% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 73.6 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
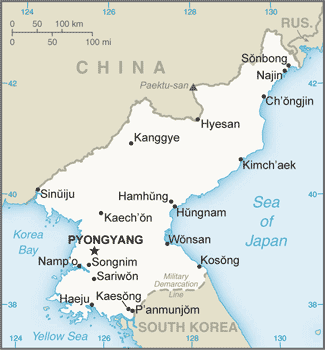
Geography17
Location
Eastern Asia, northern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Korea Bay and the Sea of Japan, between China and South Korea
Geographic coordinates
40 00 N, 127 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area
land: 120,408 sq km
water: 130 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than Virginia; slightly smaller than Mississippi
Land boundaries
border countries: China 1,352 km; South Korea 237 km; Russia 18 km
Coastline
2,495 km
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
temperate, with rainfall concentrated in summer; long, bitter winters
Terrain
mostly hills and mountains separated by deep, narrow valleys; wide coastal plains in west, discontinuous in east
Elevation
lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 m
mean elevation: 600 m
Natural resources
coal, iron ore, limestone, magnesite, graphite, copper, zinc, lead, precious metals, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
14,600 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the plains and lowlands; least-populated regions are the mountainous provinces adjacent to the Chinese border; largest concentrations are in the western provinces, particularly the municipal district of Pyongyang, and around Hungnam and Wonsan in the east
Natural hazards
volcanism: P'aektu-san (2,744 m) (also known as Baitoushan, Baegdu, or Changbaishan), on the Chinese border, is considered historically active
Geography - note
strategic location bordering China, South Korea, and Russia; mountainous interior is isolated and sparsely populated
People & Society32
Population
male: 12,884,269
female: 13,518,572
Nationality
adjective: Korean
Ethnic groups
racially homogeneous; there is a small Chinese community and a few ethnic Japanese
Languages
major-language sample(s):
월드 팩트북, 필수적인 기본 정보 제공처 (Korean)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
traditionally Buddhist and Confucian, some Christian and syncretic Chondogyo (Religion of the Heavenly Way)
Age structure
15-64 years: 68.9% (male 9,054,771/female 9,066,447)
65 years and over: 11.2% (2024 est.) (male 1,099,676/female 1,855,175)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 28.8 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 16.8 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 6 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 34.5 years
female: 37.4 years
Population growth rate
0.4% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
12.99 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
9.01 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-0.04 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the plains and lowlands; least-populated regions are the mountainous provinces adjacent to the Chinese border; largest concentrations are in the western provinces, particularly the municipal district of Pyongyang, and around Hungnam and Wonsan in the east
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.85% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.158 million PYONGYANG (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.59 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
67 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 16.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 13.8 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 70.2 years
female: 77 years
Total fertility rate
1.8 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.87 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Physician density
3.63 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
6.8% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.12 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.48 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 32.6% (2025 est.)
female: 0% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
9.3% (2017 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
68.2% (2017 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 0.1% (2017)
men married by age 18: 0% (2017)
Education expenditure
14.6% national budget (2025 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 12 years (2018 est.)
female: 12 years (2018 est.)
Government23
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
abbreviation
etymology
Government type
dictatorship, single-party communist state
Capital
geographic coordinates: 39 01 N, 125 45 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
time zone note: on 5 May 2018, North Korea reverted to UTC+9, the same time zone as South Korea
etymology: the name translates as "flat land" in Korean
Administrative divisions
provinces: Chagang, Hambuk (North Hamgyong), Hamnam (South Hamgyong), Hwangbuk (North Hwanghae), Hwangnam (South Hwanghae), Kangwon, P'yongbuk (North Pyongan), P'yongnam (South Pyongan), Ryanggang
special administration cities: Kaesong, Nampo, P'yongyang, Rason
Legal system
civil law system based on the Prussian model; influenced by Japanese traditions and Communist legal theory
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the Supreme People’s Assembly (SPA); passage requires more than two-thirds majority vote of the total SPA membership
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of North Korea
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: unknown
Suffrage
17 years of age; universal and compulsory
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2019: KIM Jong Un reelected unopposed
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislature name
legislative structure
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: judges elected by the Supreme People's Assembly for 5-year terms
subordinate courts: lower provincial courts as determined by the Supreme People's Assembly
Political parties
Korean Workers' Party or KWP (formally known as Workers' Party of Korea)
General Association of Korean Residents in Japan (Chongryon; under KWP control)
minor parties:
Chondoist Chongu Party (under KWP control)
Social Democratic Party or KSDP (under KWP control)
Diplomatic representation in the US
note: North Korea has a Permanent Mission to the UN in New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
International organization participation
ARF, FAO, G-77, ICAO, ICRM, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, NAM, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO
Independence
15 August 1945 (from Japan)
National holiday
Founding of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), 9 September (1948)
Flag
meaning: the red band stands for revolutionary traditions, the white for purity, strength, and dignity; blue for sovereignty, peace, and friendship; the red star represents socialism
National symbol(s)
red star, chollima (winged horse)
National color(s)
red, white, blue
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: PAK Se Yong/KIM Won Gyun
history: adopted 1947; North Korea's and South Korea's anthems have the same name and a similar melody, but different lyrics; the North Korean anthem is also known as "Ach'imun pinnara" (Let Morning Shine)
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Koguryo Tombs Complex; Historic Monuments and Sites in Kaesong; Mount Kumgang – Diamond Mountain from the Sea (m)
Economy14
Economic overview
one of the last centrally planned economies; hard hit by COVID-19, crop failures, international sanctions, and isolationist policies; declining growth and trade, and heavily reliant on China; poor exchange rate stability; economic data integrity issues
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $14.959 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2021: $14.982 billion (2021 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2022: $600 (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2021: $600 (2021 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$16.447 billion (2023 est.)
Agricultural products
maize, vegetables, rice, apples, cabbages, fruits, sweet potatoes, potatoes, beans, soybeans (2023)
Industries
military products; machine building, electric power, chemicals; mining (coal, iron ore, limestone, magnesite, graphite, copper, zinc, lead, and precious metals), metallurgy; textiles, food processing; tourism
Labor force
17.637 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 2.9% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 2.9% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 6.1% (2024 est.)
female: 7.4% (2024 est.)
Exports - partners
China 74%, Poland 3%, Senegal 3%, Angola 3%, Austria 3% (2023)
Exports - commodities
fake hair, iron alloys, tungsten ore, electricity, cars (2023)
Imports - partners
China 97%, Togo 1%, Peru 1%, Gabon 1%, India 0% (2023)
Imports - commodities
processed hair, plastic products, garments, fabric, soybean oil (2023)
Exchange rates
Exchange rates 2017: 135 (2017 est.)
Exchange rates 2016: 130 (2016 est.)
Exchange rates 2015: 130 (2015 est.)
Energy6
Electricity access
Electricity
consumption: 22.448 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 4.101 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 0.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 62.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
consumption: 22.105 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 10.6 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Energy consumption per capita
Communications4
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2022 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 24 (2022 est.)
Broadcast media
no independent media; radios and TVs are pre-tuned to government stations; 4 state-owned TV stations; the Korean Workers' Party owns and operates the Korean Central Broadcasting Station, and the state-run Voice of Korea operates an external broadcast service; the government prohibits listening to and jams foreign broadcasts (2019)
Internet country code
.kp
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
P
Airports
81 (2025)
Heliports
8 (2025)
Railways
standard gauge: 7,435 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge (5,400 km electrified)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 10, container ship 5, general cargo 191, oil tanker 29, other 29
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Ministry of Social Security (formerly Ministry of Public Security): Border Guard General Bureau, civil security forces; Ministry of State Security: internal security, investigations (2025)
Military expenditures
defense spending is a regime priority; between 2010 and 2020, military expenditures accounted for an estimated 20-30% of North Korea's GDP annually; spending estimates ranged from $7 billion to $11 billion annually; in 2024, North Korea announced that it would spend nearly 16% of state expenditures on defense; North Korea in the 2010s and 2020s has increasingly relied on illicit activities — including cybercrime — to generate revenue for its weapons of mass destruction and ballistic missile programs to evade US and UN sanctions
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimates vary; as many as 1.3 million active-duty Korean People's Army (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the KPA is equipped with older weapon systems acquired from China, Russia, and the former Soviet Union, as well as some domestically produced armaments; North Korea produces an array of military hardware, including armored vehicles, artillery, munitions, naval vessels, and some advanced weapons systems, such as cruise and ballistic missiles; most are copies or upgrades of older foreign supplied equipment (2025)
Military service age and obligation
compulsory military service for men (17-30 years of age) and women (17-23 years of age); service obligation is reportedly up to 10 years for men and up to 7 years for women (2025)
Military deployments
estimated 10-12,000 Russia (2025)
Military - note
in addition to the invasion of South Korea and the subsequent Korean War (1950-53), North Korea from the 1960s to the 1980s launched a number of military and subversive actions against South Korea; including skirmishes along the DMZ, overt attempts to assassinate South Korean leaders, kidnappings, the bombing of an airliner, and a failed effort in 1968 to foment an insurrection and conduct a guerrilla war in the South with more than 100 seaborne commandos; from the 1990s until 2010, the North lost two submarines and a semi-submersible boat attempting to insert infiltrators into the South (1996, 1998) and provoked several engagements in the Northwest Islands area along the disputed Northern Limit Line (NLL), including naval skirmishes between patrol boats in 1999 and 2002, the torpedoing and sinking of a South Korean Navy corvette in 2010, and the bombardment of a South Korean military installation on Yeonpyeong Island, also in 2010; since 2010, further minor incidents continue to occur periodically along the DMZ, where both the KPA and the South Korean military maintain large numbers of troops
North Korea also has a history of provocative regional military actions and posturing that are of major concern to the international community, including: proliferation of military-related items; ballistic and cruise missile development and testing; weapons of mass destruction (WMD) programs including tests of nuclear devices in 2006, 2009, 2013, 2016, and 2017; and large conventional armed forces (2025)
