Nepal
Population
31.33M
Area
147,181 km²
GDP
$42.91B
GDP Per Capita
$5,000
Pop. Density
213/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
₨Nepalese rupee(NPR)
Calling Code
+977
Timezone
UTC+05:45
Languages
Nepali
Driving Side
left
Demonym
Nepalese
Background
During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the principality of Gorkha united many of the other principalities and states of the sub-Himalayan region into a Nepali Kingdom. Nepal retained its independence after the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814-16, and the subsequent peace treaty laid the foundations for two centuries of amicable relations between Britain and Nepal. In 1951, the Nepali monarch ended the century-old system of hereditary rule and instituted a cabinet system that brought political parties into the government. That arrangement lasted until 1960, when political parties were again banned, but it was reinstated in 1990 with the establishment of a multiparty democracy within the framework of a constitutional monarchy.
A Maoist-led insurgency broke out in 1996. During the ensuing 10-year civil war between Maoist and government forces, the monarchy dissolved the cabinet and parliament. In 2001, Crown Prince DIPENDRA first massacred the royal family and then shot himself. His uncle GYANENDRA became king, and the monarchy reassumed absolute power the next year. A peace accord in 2006 led to the promulgation of an interim constitution in 2007. After a nationwide Constituent Assembly (CA) election in 2008, the newly formed CA declared Nepal a federal democratic republic, abolished the monarchy, and elected the country's first president.
When the CA failed to draft a Supreme Court-mandated constitution, then-Prime Minister Baburam BHATTARAI dissolved the CA. An interim government held elections in 2013, in which the Nepali Congress (NC) won the largest share of seats. In 2014, NC formed a coalition government with the second-place Communist Party of Nepal-Unified Marxist-Leninist (UML). Nepal's new constitution came into effect in 2015, at which point the CA became the Parliament and Khagda Prasad Sharma OLI the first post-constitution prime minister (2015-16). He resigned ahead of a no-confidence motion, and Parliament elected Communist Party of Nepal-Maoist (CPN-M) leader Pushpa Kamal DAHAL as prime minister.
The parties headed by OLI and DAHAL ran in coalition and swept the parliamentary elections in 2017, and OLI was sworn in as prime minister in 2018. OLI's efforts to dissolve parliament and hold elections were declared unconstitutional in 2021, and the opposition-supported NC leader Sher Bahadur DEUBA was named prime minister. The NC won a majority of seats in the parliamentary elections in 2022, but DAHAL then broke with the ruling coalition and partnered with OLI and the CPN-UML to become prime minister. DAHAL's first cabinet lasted about two months, until OLI withdrew his support over disagreements about ministerial assignments. In early 2023, DAHAL survived a vote of confidence and formed a coalition with the NC to remain prime minister.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑374.5% since 2006Population
↑11.6% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 70.4 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
Geography19
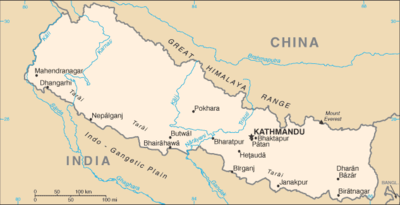
Location
Southern Asia, between China and India
Geographic coordinates
28 00 N, 84 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area
land: 143,351 sq km
water: 3,830 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than New York State
Land boundaries
border countries: China 1,389 km; India 1,770 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
varies from cool summers and severe winters in north to subtropical summers and mild winters in south
Terrain
Tarai or flat river plain of the Ganges in south; central hill region with rugged Himalayas in north
Elevation
lowest point: Kanchan Kalan 70 m
mean elevation: 2,565 m
Natural resources
quartz, water, timber, hydropower, scenic beauty, small deposits of lignite, copper, cobalt, iron ore
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
12,090 sq km (2022)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major aquifers
Indus-Ganges-Brahmaputra Basin
Population distribution
most of the population is divided nearly equally between a concentration in the southern-most plains of the Tarai region and the central hilly region; overall density is low
Natural hazards
severe thunderstorms; flooding; landslides; drought and famine depending on the timing, intensity, and duration of the summer monsoons
Geography - note
landlocked; strategic location between China and India; contains eight of world's 10 highest peaks, including Mount Everest and Kanchenjunga -- the world's tallest and third-tallest mountains -- on the borders with China and India, respectively
People & Society36
Population
male: 15,352,706
female: 15,981,696
Nationality
adjective: Nepali
Ethnic groups
Chhettri 16.5%, Brahman-Hill 11.3%, Magar 6.9%, Tharu 6.2%, Tamang 5.6%, Bishwokarma 5%, Musalman 4.9%, Newar 4.6%, Yadav 4.2%, Rai 2.2%, Pariyar 1.9%, Gurung 1.9%, Thakuri 1.7%, Mijar 1.6%, Teli 1.5%, Yakthung/Limbu 1.4%, Chamar/Harijan/Ram 1.4%, Koiri/Kushwaha 1.2%, other 20% (2021 est.)
Languages
major-language sample(s):
विश्व तथ्य पुस्तक,आधारभूत जानकारीको लागि अपरिहार्य स्रोत (Nepali)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Hindu 81.2%, Buddhist 8.2%, Muslim 5.1%, Kirat 3.2%, Christian 1.8%; less than 1%: Prakriti, Bon, Jains, Sikh (2021 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 67.8% (male 10,153,682/female 10,957,011)
65 years and over: 6.4% (2024 est.) (male 961,717/female 1,015,598)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 37.2 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 9.6 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 10.4 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 26.5 years
female: 28.6 years
Population growth rate
0.66% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
16.66 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
5.62 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-4.46 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
most of the population is divided nearly equally between a concentration in the southern-most plains of the Tarai region and the central hilly region; overall density is low
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 3.09% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.571 million KATHMANDU (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.95 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.4 years (2016 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
142 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 25.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 22.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 72.2 years
female: 73.7 years
Total fertility rate
1.82 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.88 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 8% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
1.01 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
0.4 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
4.1% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.13 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 40.3% (2025 est.)
female: 7.6% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
18.3% (2022 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
75.1% (2022 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 34.9% (2022)
men married by age 18: 7% (2022)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 10.8% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 79.8% (2019 est.)
female: 59.4% (2019 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 14 years (2023 est.)
female: 14 years (2023 est.)
Government25
Country name
conventional short form: Nepal
local long form: none
local short form: Nepal
etymology: the name probably comes from the Sanskrit term nepala, from the words for "fly down" and "house," which would refer to the villages at the base of the mountains
Government type
federal parliamentary republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 27 43 N, 85 19 E
time difference: UTC+5.75 (10.75 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name comes from the Nepalese words kath (wooden) and mandu (temple), referring to the local temples that are often still built from wood
Administrative divisions
Legal system
English common law and Hindu legal concepts
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as a bill by either house of the Federal Parliament; bills affecting a state border or powers delegated to a state must be submitted to the affected state assembly; passage of such bills requires a majority vote of that state assembly membership; bills not requiring state assembly consent require at least two-thirds majority vote by the membership of both houses of the Federal Parliament; parts of the constitution on the sovereignty, territorial integrity, independence, and sovereignty vested in the people cannot be amended
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 15 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2023: Ram Chandra POUDEL elected president; electoral college vote - Ram Chandra POUDEL (NC) 33,802, Subash Chandra NEMBANG (CPN-UML) 15,518
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name
number of seats
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Constitutional Council, a 5-member, high-level advisory body headed by the prime minister; other judges appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial Council, a 5-member advisory body headed by the chief justice; the chief justice serves a 6-year term; judges serve until age 65
subordinate courts: High Court; district courts
Political parties
Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Marxist-Leninist) or CPN-UML
Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Socialist) or CPN-US
Janamat Party
Janata Samajbaadi Party or JSP
Loktantrik Samajwadi Party or LSP
Naya Shakti Party, Nepal
Nepali Congress or NC
Nepal Mazdoor Kisan Party (Nepal Workers' and Peasants' Party) or NWPP
Rastriya Janamorcha (National People's Front)
Rastriya Prajatantra Party (National Democratic Party) or RPP
Rastriya Swatantra Party or RSP
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
International organization participation
ADB, BIMSTEC, CD, CP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNSOM, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
1768 (unified by Prithvi Narayan SHAH)
National holiday
Constitution Day, 20 September (2015)
Flag
meaning: red stands for the rhododendron (the national flower) and victory and bravery, and the blue border for peace and harmony; the two triangles are a combination of two pennants that originally symbolized the Himalaya Mountains, but today they refer to Hinduism and Buddhism, the country's two main religions; the moon stands for the serenity of the people, as well as Himalayan shade and cool weather, and the sun for the heat and higher temperatures in the rest of the country
National symbol(s)
rhododendron blossom
National color(s)
red
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Pradeep Kumar RAI/Ambar GURUNG
history: adopted 2007
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Kathmandu Valley (c); Sagarmatha National Park (n); Chitwan National Park (n); Lumbini, Buddha Birthplace (c)
Economy31
Economic overview
low-income South Asian economy; post-conflict fiscal federalism increasing stability; COVID-19 hurt trade and tourism; widening current account deficits; environmentally fragile economy from earthquakes; growing Chinese relations and investments
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $144.352 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $141.546 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 2% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 5.6% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $4,900 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $4,800 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$42.914 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 7.7% (2022 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2021: 4.1% (2021 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 11.4% (2024 est.)
services: 55.2% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
rice, vegetables, potatoes, sugarcane, maize, wheat, bison milk, milk, mangoes/guavas, bananas (2023)
Industries
tourism, carpets, textiles, small rice, jute, sugar, oilseed mills, cigarettes, cement and brick production
Industrial production growth rate
0.1% (2024 est.)
Labor force
8.435 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 10.7% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 10.9% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 19.3% (2024 est.)
female: 23.6% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
20.3% (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 24.2% (2022 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 25.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 22% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $9.1 billion (2021 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
17.5% (of GDP) (2021 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: $146.66 million (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: -$3.088 billion (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $2.258 billion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $2.106 billion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
India 67%, USA 12%, Germany 3%, China 2%, UK 2% (2023)
Exports - commodities
knotted carpets, garments, flat-rolled iron, synthetic fibers, palm oil (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $13.877 billion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $15.227 billion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
India 71%, China 17%, UAE 3%, Singapore 2%, Germany 1% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, natural gas, garments, iron reductions, broadcasting equipment (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $9.319 billion (2022 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2021: $9.639 billion (2021 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy6
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 97.7%
electrification - rural areas: 93.7%
Electricity
consumption: 9.806 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 1.1 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 1.846 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.638 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 99% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
consumption: 1.091 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 100 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 1.076 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 8 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 100 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
state operates 3 TV stations, as well as national and regional radio stations; 117 television channels are licensed, 71 of which are cable TV, 3 are distributed through Direct-To-Home (DTH) system, and 4 are digital terrestrial; 736 FM radio stations are licensed, and at least 314 of those are community stations (2019)
Internet country code
.np
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5 (2022 est.)
Transportation4
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
9N
Airports
51 (2025)
Heliports
14 (2025)
Railways
narrow gauge: 59 km (2018) 0.762-m gauge
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home Affairs: Nepal Police, Nepal Armed Police Force (APF) (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 1% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 1.3% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 95,000 active Armed Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Army's inventory includes a mix of mostly older equipment largely of British, Chinese, Indian, Russian, and South African origin; in recent years, Nepal has received limited amounts of newer hardware from several countries, including China, Indonesia, Italy, and Russia (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; upper age limit varies; no conscription (2025)
Military deployments
1240 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 1,150 Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO); 440 Golan Heights (UNDOF); 875 Lebanon (UNIFIL); 225 Liberia (UNSMIL); 100 South Sudan/Sudan (UNISFA); 1,750 (plus about 200 police) South Sudan (UNMISS) (2025)
Military - note
the British began to recruit Nepalese citizens (Gurkhas) into the East India Company Army during the Anglo-Nepalese War (1814-1816); the Gurkhas subsequently were brought into the British Indian Army and by 1914, there were 10 Gurkha regiments, collectively known as the Gurkha Brigade; following the partition of India in 1947, an agreement between Nepal, India, and Great Britain allowed for the transfer of the 10 regiments from the British Indian Army to the separate British and Indian armies; four regiments were transferred to the British Army, where they have since served continuously as the Brigade of Gurkhas; six Gurkha (aka Gorkha in India) regiments went to the new Indian Army; a seventh regiment was later added; Gurkhas are also recruited into the Singaporean Police and a special guard in the Sultanate of Brunei known as the Gurkha Reserve Unit (2025)
Transnational Issues2
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 18,671 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 467 (2024 est.)
