Ireland
Population
5.23M
Area
70,273 km²
GDP
$577.39B
GDP Per Capita
$115,300
Pop. Density
74/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
€euro(EUR)
Calling Code
+353
Timezone
UTC
Languages
English, Irish
Driving Side
left
Demonym
Irish
Background
Celtic tribes arrived in Ireland between 600 and 150 B.C. Norse invasions that began in the late 8th century finally ended when King Brian BORU defeated the Danes in 1014. Norman invasions began in the 12th century and set off more than seven centuries of Anglo-Irish struggle marked by fierce rebellions and harsh repressions. The Irish famine of the mid-19th century caused an almost 25-percent decline in the island's population through starvation, disease, and emigration. The population of the island continued to fall until the 1960s, but over the last 50 years, Ireland's high birthrate has made it demographically one of the youngest populations in the EU.
The modern Irish state traces its origins to the failed 1916 Easter Monday Uprising that galvanized nationalist sentiment. The ensuing guerrilla war led to independence from the UK in 1921 with the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the creation of the Irish Free State. The treaty was deeply controversial in Ireland, in part because it helped solidify the country's partition, with six of the 32 counties remaining in the UK as Northern Ireland. The split between pro-Treaty and anti-Treaty partisans led to the Irish Civil War (1922-23). The traditionally dominant political parties in Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fail, are de facto descendants of the opposing sides of the treaty debate. Ireland declared itself a republic in 1949 and formally left the British Dominion.
Beginning in the 1960s, deep sectarian divides between the Catholic and Protestant populations and systemic discrimination in Northern Ireland erupted into years of violence known as the Troubles. In 1998, the governments of Ireland and the UK, along with most political parties in Northern Ireland, reached the Belfast/Good Friday Agreement with the support of the US. This agreement helped end the Troubles and initiated a new phase of cooperation between the Irish and British Governments.
Ireland was neutral in World War II and continues its policy of military neutrality. Ireland joined the European Community in 1973 and the euro-zone currency union in 1999. The economic boom years of the Celtic Tiger (1995-2007) saw rapid economic growth that came to an abrupt end in 2008 with the meltdown of the Irish banking system. As a small, open economy, Ireland has excelled at courting foreign direct investment, especially from US multi-nationals, which has helped the economy recover from the financial crisis and insulated it somewhat from the economic shocks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑162.4% since 2006Population
↑26.3% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 82.9 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
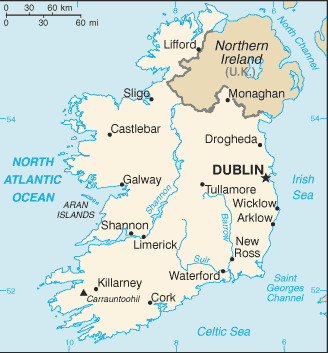
Geography17
Location
Western Europe, occupying five-sixths of the island of Ireland in the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Great Britain
Geographic coordinates
53 00 N, 8 00 W
Map references
Europe
Area
land: 68,883 sq km
water: 1,390 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than West Virginia
Land boundaries
border countries: UK 499 km
Coastline
1,448 km
Maritime claims
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Climate
temperate maritime; modified by North Atlantic Current; mild winters, cool summers; consistently humid; overcast about half the time
Terrain
mostly flat to rolling interior plain surrounded by rugged hills and low mountains; sea cliffs on west coast
Elevation
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 118 m
Natural resources
natural gas, peat, copper, lead, zinc, silver, barite, gypsum, limestone, dolomite
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2022)
Population distribution
population distribution is weighted to the eastern side of the island, with the largest concentration in and around Dublin; populations in the west are small due to mountainous land, poorer soil, and lack of transport routes
Natural hazards
rare extreme weather events
Geography - note
strategic location on major air and sea routes between North America and northern Europe; over 40% of the population resides within 100 km of Dublin
People & Society33
Population
male: 2,590,542
female: 2,642,919
Nationality
adjective: Irish
Ethnic groups
Irish 76.6%, Irish travelers 0.6%, other White 9.9%, Asian 3.3%, Black 1.5%, other (includes Arab, Roma, and persons of mixed backgrounds) 2%, unspecified 2.6% (2022 est.)
Languages
English (official, the language generally used), Irish (Gaelic or Gaeilge) (official, spoken by approximately 37.7% of the population)
Religions
Roman Catholic 69.2% (includes lapsed), Protestant 3.7% (Church of Ireland/England/Anglican/Episcopalian 2.5%, other Protestant 1.2%), Orthodox 2%, other Christian 0.9%, Muslim 1.6%, other 1.4%, agnostic/atheist 0.1%, none 14.5%, unspecified 6.7% (2022 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 65.5% (male 1,701,680/female 1,728,041)
65 years and over: 15.8% (2024 est.) (male 390,738/female 437,030)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 28.5 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 24.1 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 4.1 (2024 est.)
Median age
male: 39.7 years
female: 40.6 years
Population growth rate
0.8% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
10.95 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
7.43 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
4.48 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
population distribution is weighted to the eastern side of the island, with the largest concentration in and around Dublin; populations in the west are small due to mountainous land, poorer soil, and lack of transport routes
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 1.15% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.270 million DUBLIN (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
30.9 years (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
4 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 3.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.3 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 80.3 years
female: 83.9 years
Total fertility rate
1.72 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.83 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 22.3% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
3.88 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
2.9 beds/1,000 population (2020 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
25.3% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 4.92 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 2.88 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.29 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.82 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 19.2% (2025 est.)
female: 14.4% (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
47.1% (2022 est.)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 12.3% national budget (2021 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 19 years (2022 est.)
female: 20 years (2022 est.)
Government26
Country name
conventional short form: Ireland
local long form: none
local short form: Eire
etymology: the Irish name Eire evolved from the Gaelic name Eriu, which is possibly derived from the Old Celtic iveriu, meaning "good land;" the English name, Ireland, is a direct translation
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 53 19 N, 6 14 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: derived from the Irish words dubh (black or dark) and linn (pool), referring to the color of the Liffey River
Administrative divisions
28 counties and 3 cities*; Carlow, Cavan, Clare, Cork, Cork*, Donegal, Dublin*, Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown, Fingal, Galway, Galway*, Kerry, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Leitrim, Limerick, Longford, Louth, Mayo, Meath, Monaghan, Offaly, Roscommon, Sligo, South Dublin, Tipperary, Waterford, Westmeath, Wexford, Wicklow
Legal system
common law system based on the English model but substantially modified by customary law; Supreme Court reviews legislative acts
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as bills by Parliament; passage requires majority vote by both the Senate and House of Representatives, majority vote in a referendum, and presidential signature
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 of the previous 8 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2025: Michael MARTIN is elected taoiseach by parliament, 95 votes to 76, and is appointed taoiseach by the president
2024: Simon HARRIS is elected taoiseach by parliament, 88 votes to 69, and is appointed taoiseach by the president
2018: Michael D. HIGGINS reelected president in first round; percent of vote in first round - Michael D. HIGGINS (independent) 55.8%, Peter CASEY (independent) 23.3%, Sean GALLAGHER (independent) 6.4%, Liadh NI RIADA (Sinn Fein) 6.4%, Joan FREEMAN (independent) 6%, Gavin DUFFY (independent) 2.2%
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name
number of seats
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the prime minister and Cabinet and appointed by the president; chief justice serves in the position for 7 years; judges can serve until age 70
subordinate courts: High Court, Court of Appeal; circuit and district courts; criminal courts
Political parties
Solidarity-People Before Profit or PBP-S
Fianna Fail
Fine Gael
Green Party
Human Dignity Alliance
Independent Ireland
Labor (Labour) Party
100% Redress
Right to Change or RTC
Sinn Fein
Social Democrats
Socialist Party
The Workers' Party
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
https://www.ireland.ie/en/usa/washington/
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Independence
6 December 1921 (from the UK); 6 December 1922 (Irish Free State established); 18 April 1949 (Republic of Ireland Act enabled)
National holiday
Saint Patrick's Day, 17 March
Flag
meaning: the flag colors have no official meaning, but a common interpretation is that the green stands for the Irish nationalist tradition, orange for the Orange tradition (minority supporters of William of Orange), and white for peace or a lasting truce between the green and the orange
National symbol(s)
harp, shamrock (trefoil)
National color(s)
blue, green
National coat of arms
the coat of arms features a gold harp on a blue shield and dates back to the 13th century, although it only became official in 1945; the harp, a national symbol that Ireland adopted after gaining independence from the United Kingdom in 1921, represents the country’s history, culture, and national identity
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Peadar KEARNEY [English], Liam O RINN [Irish]/Patrick HEENEY and Peadar KEARNEY
history: adopted 1926; the song "Ireland's Call" is often used as the anthem at athletic events if citizens of Ireland and Northern Ireland are competing as a unified team
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Brú na Bóinne - Archaeological Ensemble of the Bend of the Boyne; Sceilg Mhichíl
Economy31
Economic overview
high-income, export-oriented EU economy; large multinational business sector contributes to growth and tax revenues but poses volatility risks; high living standards; strong labor market challenged by skill shortages and aging workforce
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $613.056 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $648.943 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: -5.5% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 8.6% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $115,500 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $124,500 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$577.389 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 6.3% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 7.8% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 30.8% (2024 est.)
services: 61.8% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
milk, barley, beef, wheat, potatoes, pork, oats, chicken, rapeseed, beans (2023)
Industries
pharmaceuticals, chemicals, computer hardware and software, food products, beverages and brewing; medical devices
Industrial production growth rate
-4.9% (2024 est.)
Labor force
2.857 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 4.3% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 4.6% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 11.2% (2024 est.)
female: 11% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
14% (2021 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 4% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 24.5% (2022 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2022: 0.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Remittances 2021: 0% of GDP (2021 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $108.693 billion (2022 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
16.8% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2022: $48.427 billion (2022 est.)
Current account balance 2021: $65.118 billion (2021 est.)
Exports
Exports 2022: $763.233 billion (2022 est.)
Exports 2021: $722.655 billion (2021 est.)
Exports - partners
USA 28%, Germany 11%, UK 8%, Belgium 8%, China 7% (2023)
Exports - commodities
vaccines, packaged medicine, nitrogen compounds, integrated circuits, hormones (2023)
Imports
Imports 2022: $536.882 billion (2022 est.)
Imports 2021: $500.334 billion (2021 est.)
Imports - partners
UK 20%, USA 17%, France 10%, China 7%, Germany 7% (2023)
Imports - commodities
aircraft, nitrogen compounds, vaccines, packaged medicine, integrated circuits (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $12.905 billion (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $13.039 billion (2022 est.)
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy7
Electricity access
Electricity
consumption: 32.282 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 441.615 million kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 3.89 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.489 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 1.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 37% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 2.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 3.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
exports: 76,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 1.711 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 40 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 159,000 bbl/day (2024 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 4.919 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 3.707 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 9.911 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 23 (2023 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 113 (2022 est.)
Broadcast media
publicly owned broadcaster Radio Telefis Eireann (RTE) operates 4 TV stations; commercial TV stations are available; about 75% of households use multi-channel satellite and TV services that provide access to a wide range of stations; RTE operates 4 national radio stations and has launched digital audio broadcasts on several; a number of commercial broadcast stations operate at the national, regional, and local levels (2019)
Internet country code
.ie
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 32 (2023 est.)
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
EI
Airports
100 (2025)
Heliports
10 (2025)
Railways
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 12, general cargo 32, oil tanker 1, other 49
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Irish Defense Forces (Oglaigh na h-Eireannn): Army, Air Corps, Naval Service, Reserve Defense Forces (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 0.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 0.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 0.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 0.3% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 7,500 active-duty Defense Forces (authorized establishment of 9,500) (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Irish Defense Forces have an inventory of imported weapons systems from a variety of mostly European countries (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18-38 years of age for men and women for voluntary military service (2026)
Military deployments
330 Lebanon (UNIFIL); also contributes small numbers of troops to EU, NATO, and other UN missions (2025)
Military - note
Ireland has a long-standing policy of military neutrality; however, Ireland is a signatory of the EU’s Common Security and Defense Policy and has committed a battalion of troops to the EU’s Rapid Reaction Force; Ireland is not a member of NATO but has a relationship with it going back to 1997, when it deployed personnel in support of the NATO-led peacekeeping operation in Bosnia and Herzegovina; Ireland joined NATO’s Partnership for Peace program in 1999; it has been active in UN peacekeeping operations since the 1950s (2025)
Transnational Issues1
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 48 (2024 est.)
