
European Union
Population
451.82M
Area
4,236,351 km²
GDP
$19.42T
GDP Per Capita
$54,300
Pop. Density
107/km²
Background
Within a few years, the ECSC was so successful that member states decided to further integrate their economies. In 1957, envisioning an "ever closer union," the Treaties of Rome created the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom), which eliminated trade barriers among the six member states to create a common market. In 1967, the institutions of all three communities were formally merged into the European Community (EC), creating a single Commission, a single Council of Ministers, and a legislative body known today as the European Parliament. Members of the European Parliament were initially selected by national parliaments, but direct elections began in 1979 and have been held every five years since.
In 1973, the first enlargement of the EC added Denmark, Ireland, and the UK. The 1980s saw further membership expansion, with Greece joining in 1981 and Spain and Portugal in 1986. The 1992 Treaty of Maastricht laid the basis for further cooperation in foreign and defense policy and judicial and internal affairs, as well as the creation of an economic and monetary union -- including a common currency. The Maastricht Treaty created the European Union (EU), at the time standing alongside the EC. In 1995, Austria, Finland, and Sweden joined the EU/EC, raising the total number of member states to 15. On 1 January 1999, the new euro currency was launched in world markets and became the unit of exchange for all EU member states except Denmark, Sweden, and the UK. In 2002, citizens of the 12 participating member states began using euro banknotes and coins.
In an effort to ensure that the EU could function efficiently with an expanded membership, the Treaty of Nice in 2000 set forth rules to streamline the size and procedures of the EU's institutions. An effort to establish a "Constitution for Europe," growing out of a Convention held in 2002-2003, foundered when it was rejected in referenda in France and the Netherlands in 2005. A subsequent effort in 2007 incorporated many features of the rejected draft Constitutional Treaty, while also making a number of substantive as well as symbolic changes. The new treaty, referred to as the Treaty of Lisbon, sought to amend existing treaties rather than replace them. The treaty was approved at a conference of member states, and after all member states ratified, the Lisbon Treaty came into force on 1 December 2009, at which point the EU officially replaced and succeeded the EC.
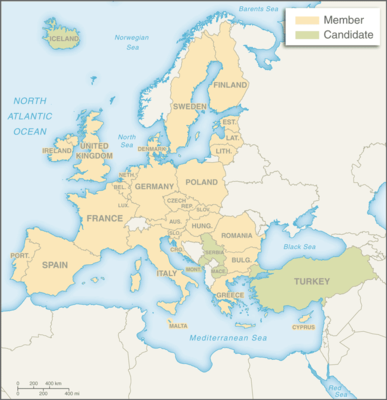
Ten new countries joined the EU in 2004 -- Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia. Bulgaria and Romania joined in 2007 and Croatia in 2013. UK citizens on 23 June 2016 narrowly voted to leave the EU; the formal exit, widely known as "Brexit," took place on 31 January 2020. The EU and the UK negotiated a withdrawal agreement that included a status quo transition period through December 2020, when the follow-on EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement was concluded. Current EU membership stands at 27. Eight of the newer member states -- Croatia, Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Slovakia, and Slovenia -- have now adopted the euro, bringing total euro-zone membership to 20.
Geography13
Location
Europe between the North Atlantic Ocean in the west and Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine to the east
Map references
Europe
Area
Area - comparative
less than one-half the size of the United States
Land boundaries
border countries: Albania 212 km; Andorra 118 km; Belarus 1,176 km; Bosnia and Herzegovina 956 km; Holy See 3 km; Liechtenstein 34 km; North Macedonia 396 km; Moldova 683 km; Monaco 6 km; Montenegro 19 km; Norway 2,375 km; Russia 2,435 km; San Marino 37 km; Serbia 1,353 km; Switzerland 1,729 km; Turkey 415 km; United Kingdom 499 km; Ukraine 1,324 km
Coastline
53,563.9 km
Climate
cold temperate; potentially subarctic in the north to temperate; mild wet winters; hot dry summers in the south
Terrain
fairly flat along Baltic and Atlantic coasts; mountainous in the central and southern areas
Elevation
lowest point: Zuidplaspolder, Netherlands -7 m
Natural resources
iron ore, natural gas, petroleum, coal, copper, lead, zinc, bauxite, uranium, potash, salt, hydropower, arable land, timber, fish
Irrigated land
154,539.82 sq km (2011 est.)
Population distribution
population distribution varies considerably from country to country but tends to follow a pattern of coastal and river settlement, with urban agglomerations forming large hubs; the area in and around the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg (known collectively as Benelux), is the most densely populated area in the EU
Natural hazards
flooding along coasts; avalanches in mountainous area; earthquakes in the south; volcanic eruptions in Italy; periodic droughts in Spain; ice floes in the Baltic Sea region
People & Society18
Population
male: 220,631,332
female: 231,183,980
Languages
Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, Swedish
Religions
Roman Catholic 41%, Orthodox 10%, Protestant 9%, other Christian 4%, Muslim 2%, other 4% (includes Jewish, Sikh, Buddhist, Hindu), atheist 10%, non-believer/agnostic 17%, unspecified 3% (2019 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 63.5% (male 143,874,460/female 143,104,994)
65 years and over: 22% (2024 est.) (male 43,150,599/female 56,093,868)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 22.8 (2024)
elderly dependency ratio: 34.5 (2024)
potential support ratio: 3 (2024)
Median age
male: 42.6 years
female: 45.5 years
Population growth rate
0.1% (2021 est.)
Birth rate
8.9 births/1,000 population (2024 est.)
Death rate
11.2 deaths/1,000 population (2024 est.)
Net migration rate
-2.85 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Population distribution
population distribution varies considerably from country to country but tends to follow a pattern of coastal and river settlement, with urban agglomerations forming large hubs; the area in and around the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg (known collectively as Benelux), is the most densely populated area in the EU
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Infant mortality rate
Life expectancy at birth
male: 72.98 years
female: 82.51 years
Total fertility rate
1.54 children born/woman (2024 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.75 (2024 est.)
Health expenditure
10.9% of GDP (2021)
Education expenditure
5% of GDP (2020 est.)
Government20
Union name
abbreviation: EU
Government type
a hybrid and unique intergovernmental and supranational organization
Capital
geographic coordinates: (Brussels) 50 50 N, 4 20 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1 hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
time zone note: the 27 European Union member states are spread across three time zones
Member states
27 countries: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
13 overseas countries and territories: 1 with Denmark (Greenland), 6 with France (French Polynesia, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, New Caledonia, Saint Barthelemy, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna), and 6 with the Netherlands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curacao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten); all are part of the Overseas Countries and Territories Association (OCTA)
Legal system
unique supranational system in which EU treaties and EU law have primacy over member-state law
Constitution
amendment process: EU treaties can be amended in several ways:
1) Ordinary Revision Procedure (for key amendments to the treaties); initiated by an EU member state, the European Parliament, or the European Commission; after the proposal is adopted by the European Council, a conference of national government representatives then reviews the proposal; passage requires ratification by all EU member states
2) Simplified Revision Procedure (for amendment of EU internal policies and actions); passage of a proposal requires unanimous European Council vote after European Council consultation with the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the European Central Bank (if the amendment concerns monetary matters) and requires ratification by all EU member states
3) Passerelle Clause; allows the alteration of a legislative procedure without a formal amendment of the treaties
4) Flexibility Clause; permits the EU to decide in subject areas where EU competences have not been explicitly granted in the treaties but are necessary to the attainment of treaty objectives
Suffrage
18 years of age (16 years in Austria); universal; voting for the European Parliament occurs in each member state
Executive branch
European Council - composed of member-state heads of state or government, along with the president of the European Commission; meets at least four times a year to issue general policy guidance; the president of the European Council is appointed by leaders of the EU member states for a 2 1/2 year term, renewable once
president: António Costa (since 1 December 2024)
Council of the European Union - consists of member-state officials, ranging from working-level diplomats to cabinet ministers in specific policy fields such as foreign affairs, agriculture, or economy; has policymaking, coordinating, and legislative functions
president: the six-month presidency rotates among the member states
European Commission - composed of 27 commissioners (one from each member state), including the president; the president assigns each commissioner one or more policy areas, called portfolios; the Commission has the sole right to initiate EU legislation, except for foreign and security/defense policy, and is responsible for monitoring the application of EU law, implementing/executing the EU budget, negotiating in certain policy areas, and ensuring the EU's external representation in some policy areas; the president is nominated for a 5-year term by the European Council and confirmed by the European Parliament; the European Parliament also confirms the entire Commission for a 5-year term
president: Ursula von der Leyen (since 1 December 2019)
Legislative branch
legislature name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the common consent of the member states to serve 6-year renewable terms
Political parties
European Conservatives and Reformists or ECR
Greens/European Free Alliance or Greens/EFA
European People's Party or EPP
Europe of Sovereign Nations or ESN
Patriots for Europe or PfE
Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats or S&D
Renew Europe or Renew (formerly Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe or ALDE)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 2175 K Street NW, Washington, DC 20037
telephone: [1] (202) 862-9500
FAX: [1] (202) 429-1766
email address and website:
[email protected]
Delegation of the European Union to the United States of America | EEAS (europa.eu)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: Zinnerstraat - 13 - Rue Zinner, B-1000 Brussels
mailing address: use embassy street address
telephone: [32] (2) 811-4100
email address and website:
https://useu.usmission.gov/
International organization participation
ARF, ASEAN (dialogue member), Australian Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CERN, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-7, G-10, G-20, IDA, IEA, IGAD (partners), LAIA (observer), NSG (observer), OAS (observer), OECD, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SICA (observer), UN (observer), UNRWA (observer), WCO, WTO, ZC (observer)
Independence
7 February 1992 (Maastricht Treaty signed establishing the European Union); 1 November 1993 (Maastricht Treaty entered into force)
National holiday
Europe Day (also known as Schuman Day), 9 May (1950)
Flag
meaning: the number of stars is fixed and does not correspond to the number of member states
National symbol(s)
a circle of 12 five-pointed golden-yellow stars on a blue field
National color(s)
blue, yellow
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: no lyrics/Ludwig VAN BEETHOVEN, arranged by Herbert VON KARAJAN
history: adopted 1985; the anthem is meant to represent all of Europe rather than just the organization, conveying the ideals of peace, freedom, and unity
Economy24
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $24.17 trillion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $24.036 trillion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 0.5% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 3.5% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $53,800 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $53,700 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$19.423 trillion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 6.3% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 8.8% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 22.1% (2024 est.)
services: 66.1% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, sugar beets, maize, potatoes, barley, grapes, pork, rapeseed, tomatoes (2022)
Industries
among the world's largest and most technologically advanced regions, the EU industrial base includes: ferrous and non-ferrous metal production and processing, metal products, petroleum, coal, cement, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, rail transportation equipment, passenger and commercial vehicles, construction equipment, industrial equipment, shipbuilding, electrical power equipment, machine tools and automated manufacturing systems, electronics and telecommunications equipment, fishing, food and beverages, furniture, paper, textiles
Industrial production growth rate
-0.7% (2024 est.)
Labor force
221.391 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 6.1% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 6.2% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 16% (2024 est.)
female: 16% (2024 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 0.8% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 0.8% of GDP (2022 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
19.8% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $9.689 trillion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $9.425 trillion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
US 20%, UK 12%, China 10%, Switzerland 7%, Turkey 4% (2023)
Exports - commodities
cars, packaged medicine, refined petroleum, vehicle parts/accessories, vaccines (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $8.978 trillion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $9.072 trillion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
China 21%, US 14%, UK 7%, Switzerland 6%, Norway 5% (2023)
Imports - commodities
cars, crude petroleum, natural gas, refined petroleum, vehicle parts/accessories (2023)
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy8
Electricity access
Electricity
consumption: 2.511 trillion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 407.824 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 405.154 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 169.694 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels
nuclear
solar
wind
hydroelectricity
geothermal
biomass and waste
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors under construction: 1 (2025)
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 97.63GW (2025 est.)
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 75 (2025)
Coal
consumption: 398.817 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 32.326 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 127.304 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 84.193 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 11.022 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 335.326 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 100.238 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 396.993 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications5
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 36 (2022 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 124 (2022 est.)
Internet country code
.eu
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 39 (2022 est.)
Transportation3
Airports
5,211 (2025)
Heliports
2,069 (2025)
Railways
Military & Security4
Military and security forces
the Political and Security Committee (PSC), which meets at the ambassadorial level as a preparatory body for the Council of the EU; it assists with defining policies and preparing a crisis response
the European Union Military Committee (EUMC) is the EU's highest military body; it is composed of the chiefs of defense (CHODs) of the Member States, who are regularly represented by their permanent Military Representatives; the EUMC provides the PSC with advice and recommendations on all military matters within the EU
the Committee for Civilian Aspects of Crisis Management (CIVCOM) provides advice and recommendations to the PSC in parallel with the EUMC on civilian aspects of crisis management
the Politico-Military Group (PMG) provides advice and recommendations to the PSC on political aspects of EU military and civil-military issues, including concepts, capabilities and operations and missions, and monitors implementation
other bodies set up under the CSDP include the Security and Defense Policy Directorate (SECDEFPOL), the Integrated approach for Security and Peace Directorate (ISP), the EU Military Staff (EUMS), the Civilian Planning and Conduct Capability (CPCC), the Civilian Operations Headquarters (CivOpsHQ), the Military Planning and Conduct Capability (MPCC), the European Defense Agency (EDA), the European Security and Defense College (ESDC), the EU Institute for Security Studies, the EU Satellite Center, the Peace, Partnerships and Crisis Management Directorate (PCM) (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 1.8% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.6% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 1.6% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military deployments
since 2003, the EU has launched more than 30 civilian and military crisis-management, advisory, and training missions in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, as well as counter-piracy operations off the coast of Somalia and a naval operation in the Mediterranean to disrupt human smuggling and trafficking networks and prevent the loss of life at sea (2025)
Military - note
there are no permanent standing EU forces, but Europe has a variety of multinational military organizations that may be deployed through the EU, in a NATO environment, upon the mandate of the participating countries, or upon the mandate of other international organizations, such as the UN or OSCE including:
the EU Rapid Deployment Capacity (EU RDC) was declared operational in May 2025; the RDC's purpose is to enable the EU to respond to different crisis scenarios by providing a flexible and scalable military instrument of up to 5,000 troops that can be deployed in a swift manner; missions could include capacity building, conflict prevention, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, rescue and evacuation, or stabilization; the use of the RDC is subject to a unanimous decision by the EU Member States
EU Battlegroups (BGs) are rapid reaction multinational army units that form a key part of the EU's capacity to respond to crises and conflicts; their deployment is subject to a unanimous decision by the European Council; BGs typically consists of 1,500-2,000 troops organized around an infantry battalion depending on the mission; the troops and equipment are drawn from EU member states and under the direction of a lead nation; two BGs are always on standby for a period of six months; the BGs were declared operational in 2007 but have never been used operationally due to political and financial obstacles
the European Corps (Eurocorps) is an independent multinational land force corps headquarters composed of personnel from six framework nations and five associated nations; the corps has no standing operational units; during a crisis, units would be drawn from participating states, and the corps would be placed at the service of the EU and NATO; Eurocorps was established in 1992 by France and Germany; Belgium (1993), Spain (1994), and Luxembourg (1996) joined over the next few years; Poland joined in 2022; Greece and Turkey (since 2002), Italy, Romania, and Austria (since 2009, 2016, and 2021 respectively) participate as associated nations; Eurocorps is headquartered in France
the European Gendarmerie Force (EURGENDFOR) is an operational, pre-organized, and rapidly deployable European gendarmerie/police force; it is not established at the EU level, but is capable of performing police tasks, including law enforcement, stability operations, and training in support of the EU, the UN, OSCE, NATO, and other international organizations or ad hoc coalitions; member state gendarmeries include those of France, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, and Spain; the Lithuanian Public Security Service is a partner, while Turkey's Gendarmerie is an observer force
the European Medical Corps (EMC) was set up in the aftermath of the Ebola crisis in West Africa in 2014 to enable the deployment of teams and equipment from EU member states to provide medical assistance and public health expertise in response to emergencies inside and outside the EU; 12 European states have committed teams and equipment to the EMC
the European Medical Command (EMC) was formed to provide a standing EU medical capability, increase medical operational readiness, and improve interoperability amongst the participating EU members; it operates closely with the NATO Framework Nations Concept’s Multinational Medical Coordination Center (MMCC) under a single administrative and infrastructural framework (MMCC/EMC); the EMC was declared operational in May 2022
the European Air Transport Command (EATC) is a single multinational command for more than 150 military air mobility assets from seven member states, including transport, air-to-air refueling, and aeromedical evacuation; the EATC headquarters is located in the Netherlands, but the air assets remain located at member national air bases; the EATC was established in 2010
the European Air Group (EAG) is an independent organization formed by the air forces of its seven member nations (Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, and the UK) that is focused on improving interoperability between the air forces of EAG members and its 14 partner and associate nations; it was established in the late 1990s and is headquartered in the UK
the European Maritime Force (EUROMARFOR or EMF) is a four-nation (France, Italy, Portugal, and Spain), non-standing naval force with the ability to carry out naval, air, and amphibious operations; EUROMARFOR was formed in 1995 to conduct missions such as crisis response, humanitarian missions, peacekeeping, peace enforcement, and sea control; it can deploy under EU, NATO, or UN mandate, but also as long as the four partner nations agree
the Combined Joint Expeditionary Force (CJEF) is a deployable, combined France-UK military force of up to 10,000 personnel for use in a wide range of crisis scenarios, up to and including high intensity combat operations; the CJEF has no standing forces but would be available at short notice for French-UK bilateral, NATO, EU, UN, or other operations; it was established in 2010 and declared operational in 2020
the 1st German/Netherlands (Dutch) Corps is a combined army corps headquarters that has the ability to conduct operations under the command and control of Germany and the Netherlands, NATO, or the EU; in peacetime, approximately 1,100 Dutch and German soldiers are assigned, but during a crisis up to 80,000 troops may be assigned; it was formed in 1995 and is headquartered in Germany
the Lithuanian-Polish-Ukrainian Brigade (LITPOLUKRBRIG) is comprised of an international staff, three battalions, and specialized units; units affiliated with the multinational brigade remain within the structures of the armed forces of their respective countries until the brigade is activated for participation in an international operation; it was formed in 2014 and is headquartered in Poland (2025)
Compare European Union
See how European Union compares to other countries side by side.
Compare Countries