Burma
Union of Burma
Population
57.93M
Area
676,578 km²
GDP
$74.08B
GDP Per Capita
$5,300
Pop. Density
86/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
KsBurmese kyat(MMK)
Calling Code
+95
Timezone
UTC+06:30
Languages
Burmese
Driving Side
right
Demonym
Burmese
Background
In 1990, the military regime permitted an election but then rejected the results after the main opposition National League for Democracy (NLD) and its leader AUNG SAN SUU KYI (ASSK) won in a landslide. The military regime placed ASSK under house arrest until 2010. In 2007, rising fuel prices in Burma led pro-democracy activists and Buddhist monks to launch a "Saffron Revolution" consisting of large protests against the regime, which violently suppressed the movement. The regime prevented new elections until it had drafted a constitution designed to preserve the military's political control; it passed the new constitution in its 2008 referendum. The regime conducted an election in 2010, but the NLD boycotted the vote, and the military’s political proxy, the Union Solidarity and Development Party, easily won; international observers denounced the election as flawed.
Burma nonetheless began a halting process of political and economic reforms. ASSK's return to government in 2012 eventually led to the NLD's sweeping victory in the 2015 election. With ASSK as the de facto head of state, Burma’s first credibly elected civilian government drew international criticism for blocking investigations into Burma’s military operations -- which the US Department of State determined constituted genocide -- against its ethnic Rohingya population. When the 2020 elections resulted in further NLD gains, the military denounced the vote as fraudulent. In 2021, the military's senior leader General MIN AUNG HLAING launched a coup that returned Burma to authoritarian rule, with military crackdowns that undid reforms and resulted in the detention of ASSK and thousands of pro-democracy actors.
Pro-democracy organizations have formed in the wake of the coup, including the National Unity Government (NUG). Members of the NUG include representatives from the NLD, ethnic minority groups, and civil society. In 2021, the NUG announced the formation of armed militias called the People's Defense Forces (PDF) and an insurgency against the military junta. As of 2024, PDF units across the country continued to fight the regime with varying levels of support from and cooperation with the NUG and other anti-regime organizations, including armed ethnic groups that have been fighting the central government for decades.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑410.7% since 2006Population
↑14.1% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 66.9 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
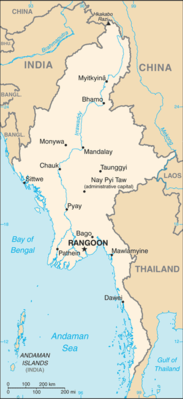
Geography19
Location
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Bangladesh and Thailand
Geographic coordinates
22 00 N, 98 00 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Area
land: 653,508 sq km
water: 23,070 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Texas
Land boundaries
border countries: Bangladesh 271 km; China 2,129 km; India 1,468 km; Laos 238 km; Thailand 2,416 km
Coastline
1,930 km
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures, lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April)
Terrain
central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands
Elevation
lowest point: Andaman Sea/Bay of Bengal 0 m
mean elevation: 702 m
Natural resources
petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas, hydropower, arable land
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
17,140 sq km (2020)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km)
Population distribution
population concentrated along coastal areas and in general proximity to the shores of the Irrawaddy River; the extreme north is relatively underpopulated
Natural hazards
destructive earthquakes and cyclones; flooding and landslides common during rainy season (June to September); periodic droughts
Geography - note
strategic location near major Indian Ocean shipping lanes; the north-south flowing Irrawaddy River is the country's largest and most important commercial waterway
People & Society36
Population
male: 28,591,467
female: 29,340,251
Nationality
adjective: Burmese
Ethnic groups
Burman (Bamar) 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Indian 2%, Mon 2%, other 5%
Languages
major-language sample(s):
ကမ္ဘာ့အချက်အလက်စာအုပ်- အခြေခံအချက်အလက်တွေအတွက် မရှိမဖြစ်တဲ့ အရင်းအမြစ် (Burmese)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Buddhist 87.9%, Christian 6.2%, Muslim 4.3%, Animist 0.8%, Hindu 0.5%, other 0.2%, none 0.1% (2014 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 68.5% (male 19,420,361/female 19,998,625)
65 years and over: 7.1% (2024 est.) (male 1,770,293/female 2,296,804)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 35 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 10.7 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 9.3 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 29.9 years
female: 31.6 years
Population growth rate
0.69% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
15.44 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
7.17 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-1.36 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated along coastal areas and in general proximity to the shores of the Irrawaddy River; the extreme north is relatively underpopulated
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 1.85% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
5.610 million RANGOON (Yangon) (capital), 1.532 million Mandalay (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
24.7 years (2015/16 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
185 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 35.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 28.5 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 68.5 years
female: 72.1 years
Total fertility rate
1.95 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.95 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 2.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.76 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
1.1 beds/1,000 population (2020 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
5.8% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.55 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 68.1% (2025 est.)
female: 17.1% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
19.5% (2018 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
58% (2019 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 16% (2016)
men married by age 18: 5% (2016)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 9.7% national budget (2019 est.)
Literacy
male: 94.7% (2020 est.)
female: 92.7% (2020 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 11 years (2018 est.)
female: 12 years (2018 est.)
Government23
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
former
etymology
Government type
military regime
Capital
geographic coordinates: 16 48 N, 96 10 E
time difference: UTC+6.5 (11.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: Rangoon/Yangon derives from the Burmese words yan and koun, commonly translated as "end of strife"; Nay Pyi Taw translates as "abode of kings"
Administrative divisions
regions: Ayeyarwady (Irrawaddy), Bago, Magway, Mandalay, Sagaing, Tanintharyi, Yangon (Rangoon)
states: Chin, Kachin, Kayah, Karen, Mon, Rakhine, Shan
union territory: Nay Pyi Taw
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law (as introduced in codifications designed for colonial India) and customary law
Constitution
amendment process: proposals require at least 20% approval by the Assembly of the Union membership; passage of amendments to sections of the constitution on basic principles, government structure, branches of government, state emergencies, and amendment procedures requires 75% approval by the Assembly and approval in a referendum by absolute majority of registered voters; passage of amendments to other sections requires only 75% Assembly approval; military granted 25% of parliamentary seats by default
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: both parents must be citizens of Burma
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: none
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
2020: the National League for Democracy (NLD) won 396 seats across both houses -- well above the 322 required for a parliamentary majority -- but on 1 February 2021, the military claimed the results of the election were illegitimate and deposed State Counsellor AUNG SAN SUU KYI and President WIN MYINT of the NLD, causing military-affiliated Vice President MYINT SWE (USDP) to become acting president; MYINT SWE subsequently handed power to coup leader MIN AUNG HLAING; WIN MYINT and other key leaders of the ruling NLD party were placed under arrest after the military takeover
2018: WIN MYINT elected president in an indirect by-election held on 28 March 2018 after the resignation of HTIN KYAW; Assembly of the Union vote for president - WIN MYINT (NLD) 403, MYINT SWE (USDP) 211, HENRY VAN THIO (NLD) 18, 4 votes canceled (636 votes cast)
expected date of next election
state counsellor
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
most recent election date: 28 December 2025
expected date of next election: on 31 July 2025, the military government announced that it was preparing for elections to be held in late December 2025
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: chief justice and judges nominated by the president, with approval of the Lower House, and appointed by the president; judges normally serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: High Courts of the Region; High Courts of the State; Court of the Self-Administered Division; Court of the Self-Administered Zone; district and township courts; special courts (for juvenile, municipal, and traffic offenses); courts martial
Political parties
the 9 parties included:
Democratic Party of National Politics (DNP)
Myanmar Farmers Development Party (MFDP)
National Democratic Force Party (NDF)
National Unity Party (NUP)
People’s Party
People’s Pioneer Party (PPP)
Shan and Ethnic Democratic Party (SEDP)
Union Solidarity and Development Party (USDP)
Women’s Party (Mon)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
International organization participation
ADB, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, CP, EAS, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), NAM, OPCW (signatory), SAARC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
4 January 1948 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 4 January (1948); Union Day, 12 February (1947)
Flag
history: the design revives the triband colors that Burma used from 1943 to 1945, during the Japanese occupation
National symbol(s)
chinthe (mythical lion)
National color(s)
yellow, green, red, white
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: SAYA TIN
history: adopted 1948
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Pyu Ancient Cities; Bagan
Economy31
Economic overview
slowly recovering Southeast Asian economy; household incomes weaken domestic consumption; growing trade deficit; declining employment; high inflation and reduced currency power; agriculture sector remains most stable
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $290.381 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $287.624 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 1% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 4% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $5,400 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $5,400 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$74.08 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2018: 6.9% (2018 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2017: 4.6% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 37.8% (2024 est.)
services: 41.4% (2024 est.)
Agricultural products
rice, sugarcane, vegetables, beans, maize, groundnuts, plantains, fruits, coconuts, onions (2023)
Industries
agricultural processing; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; cement, construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer; oil and natural gas; garments; jade and gems
Industrial production growth rate
-0.2% (2024 est.)
Labor force
22.742 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 3.1% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 3.1% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 10.5% (2024 est.)
female: 9.4% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
24.8% (2017 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 0.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 25.5% (2017 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2022: 2% of GDP (2022 est.)
Remittances 2021: 1.9% of GDP (2021 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $10.22 billion (2019 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
6% (of GDP) (2019 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2018: -$2.561 billion (2018 est.)
Current account balance 2017: -$4.917 billion (2017 est.)
Exports
Exports 2019: $17.523 billion (2019 est.)
Exports 2018: $15.728 billion (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
China 32%, Thailand 16%, Japan 7%, Germany 6%, India 5% (2023)
Exports - commodities
garments, natural gas, dried legumes, rare-earth metal compounds, precious stones (2023)
Imports
Imports 2019: $17.356 billion (2019 est.)
Imports 2018: $18.664 billion (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 40%, Thailand 18%, Singapore 15%, Indonesia 4%, Malaysia 4% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, synthetic fabric, fertilizers, crude petroleum, fabric (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $8.182 billion (2022 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2021: $9.103 billion (2021 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Exchange rates 2019
Energy7
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 93.9%
electrification - rural areas: 62.8%
Electricity
consumption: 23.625 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 200 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.855 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 36.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
consumption: 907,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 221,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 67,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 252 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 122,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 139 million barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 4.241 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 9.29 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 219.822 million cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 637.129 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2024 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 114 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
government controls all domestic broadcast media; 2 state-controlled TV stations, with 1 controlled by the armed forces; 2 pay-TV stations are joint state-private ventures; 1 state-controlled radio station; 9 FM stations are joint state-private ventures; several international broadcasts are available in some areas; the Voice of America (VOA), Radio Free Asia (RFA), BBC Burmese service, the Democratic Voice of Burma (DVB), and Radio Australia use shortwave to broadcast; VOA, RFA, and DVB produce daily TV news programs that are transmitted by satellite; in 2017, the government granted licenses to 5 private broadcasters for digital free-to-air TV channels to be operated in partnership with government-owned Myanmar Radio and Television (MRTV); after the 2021 military coup, the regime revoked the media licenses of most independent outlets, including the free-to-air licenses for DVB and Mizzima (2022)
Internet country code
.mm
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2023 est.)
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
XY
Airports
74 (2025)
Heliports
6 (2025)
Railways
narrow gauge: 5,031 km (2008) 1.000-m gauge
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 1, general cargo 44, oil tanker 5, other 51
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security6
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home Affairs: Burma (People's) Police Force, Border Guard Forces/Police (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2022: 3.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 3.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 3% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military Expenditures 2019: 4.1% of GDP (2019 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; estimated 150,000 active military personnel (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Burmese military's inventory is comprised of mostly Chinese, Russian, or Soviet-era armaments; Burma's defense industry is involved in shipbuilding and the production of ground force equipment based largely on Chinese and Russian designs (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18-35 years of age (men) and 18-27 years of age (women) for voluntary and conscripted military service; 24-month service obligation; conscripted professional men (ages 18-45) and women (ages 18-35), including doctors, engineers, and mechanics, serve up to 36 months; service terms may be extended to 60 months in an officially declared emergency (2025)
Military - note
the Tatmadaw's primary operational focus is internal security, and it is conducting counterinsurgency operations against anti-regime forces that launched an armed rebellion following the 2021 coup and an array of ethnic armed groups (EAGs); as of 2024, the Tatmadaw was reportedly engaged in combat operations in 10 of its 14 regional commands
EAGs have been fighting for self-rule against the Burmese Government since 1948; they range in strength from a few hundred fighters up to an estimated 30,000; some are organized along military lines with "brigades" and "divisions" and armed with heavy weaponry, including artillery; they control large tracts of the country’s territory, primarily in the border regions; key groups include the United Wa State Army, Karen National Union, Kachin Independence Army, Arakan Army, Ta’ang National Liberation Army, and the Myanmar Nationalities Democratic Alliance Army
the opposition National Unity Government claims its armed wing, the People's Defense Force (PDF), has more than 60,000 fighters loosely organized into battalions; in addition, several EAGs have cooperated with the NUG and supported local PDF groups (2024)
Transnational Issues3
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 619,429 (2024 est.)
Trafficking in persons
Illicit drugs
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
