Bhutan
Kingdom of Bhutan
Population
892.9K
Area
38,394 km²
GDP
$3.02B
GDP Per Capita
$14,600
Pop. Density
23/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
Nu.Bhutanese ngultrum(BTN)
Calling Code
+975
Timezone
UTC+06:00
Languages
Dzongkha
Driving Side
left
Demonym
Bhutanese
Background
In 2005, King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK unveiled the draft of Bhutan's first constitution -- which introduced major democratic reforms -- and held a national referendum for its approval. The King abdicated the throne in 2006 in favor of his son, Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK. In 2007, India and Bhutan renegotiated their treaty, eliminating the clause that stated that Bhutan would be "guided by" India in conducting its foreign policy, although Thimphu continues to coordinate closely with New Delhi. In 2008, Bhutan held its first parliamentary election in accordance with the constitution. Bhutan experienced a peaceful turnover of power following a parliamentary election in 2013, which resulted in the defeat of the incumbent party. In 2018, the incumbent party again lost the parliamentary election. In 2024, of the more than 100,000 ethnic Nepali -- predominantly Lhotshampa -- refugees who fled or were forced out of Bhutan in the 1990s, about 6,500 remain displaced in Nepal.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑219.5% since 2006Population
↑18.0% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 73.0 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
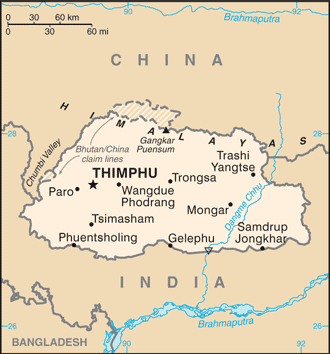
Geography16
Location
Southern Asia, between China and India
Geographic coordinates
27 30 N, 90 30 E
Map references
Asia
Area
land: 38,394 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than Maryland; about one-half the size of Indiana
Land boundaries
border countries: China 477 km; India 659 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
varies; tropical in southern plains; cool winters and hot summers in central valleys; severe winters and cool summers in Himalayas
Terrain
mostly mountainous with some fertile valleys and savanna
Elevation
lowest point: Drangeme Chhu 97 m
mean elevation: 2,220 m
Natural resources
timber, hydropower, gypsum, calcium carbonate
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
320 sq km (2012)
Natural hazards
violent storms from the Himalayas are the source of the country's Bhutanese name, which translates as Land of the Thunder Dragon; frequent landslides during the rainy season
Geography - note
landlocked; strategic location between China and India; controls several key Himalayan mountain passes
People & Society33
Population
male: 461,679
female: 431,198
Nationality
adjective: Bhutanese
Ethnic groups
Ngalop (also known as Bhote) 50%, ethnic Nepali 35% (predominantly Lhotshampas), indigenous or migrant tribes 15%
Languages
Sharchopkha 28%, Dzongkha (official) 24%, Lhotshamkha 22%, other 26% (includes foreign languages) (2005 est.)
Religions
Lamaistic Buddhist 75.3%, Indian- and Nepali-influenced Hinduism 22.1%, other 2.6% (2005 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 70.2% (male 322,497/female 298,324)
65 years and over: 6.7% (2024 est.) (male 30,397/female 28,576)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 32.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 9.7 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 10.3 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 31.1 years
female: 30.3 years
Population growth rate
0.93% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
15.05 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
5.75 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 2.52% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
203,000 THIMPHU (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.08 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.06 male(s)/female
total population: 1.07 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
47 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 24.6 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 23.9 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 72.5 years
female: 75 years
Total fertility rate
1.75 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.85 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 6.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.55 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Hospital bed density
2.2 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
6.4% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 26.1% (2025 est.)
female: 9.8% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
8.7% (2023 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
62% (2022 est.)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 22.2% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 73.4% (2022 est.)
female: 57% (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 12 years (2022 est.)
female: 14 years (2022 est.)
Government24
Country name
conventional short form: Bhutan
local long form: Druk Gyalkhap
local short form: Druk Yul
etymology: name may derive from the Sanskrit words bhoṭa, the name for Tibet, and anta, meaning "end" -- a reference to Bhutan's location at the southernmost end of Tibet; the local Dzongkha name Druk Yul means "Land of the Dragon"
Government type
constitutional monarchy
Capital
geographic coordinates: 27 28 N, 89 38 E
time difference: UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the origins of the name are unclear; the traditional explanation, dating to the 14th century, is that thim means "dissolve" and phu means "rock," in reference to a local deity who dissolved before a traveler's eyes, becoming a part of the rock on which the present city stands
Administrative divisions
Legal system
civil law based on Buddhist religious law
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as a motion by simple majority vote in a joint session of Parliament; passage requires at least a three-fourths majority vote in a joint session of the next Parliament and assent by the king
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Bhutan
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Tshering TOBGAY (since 28 January 2024)
cabinet: Council of Ministers or Lhengye Zhungtshog members nominated by the monarch in consultation with the prime minister and approved by the National Assembly; members serve 5-year terms
election/appointment process: the monarchy is hereditary but can be removed by a two-thirds vote of Parliament; leader of the majority party in Parliament is nominated as the prime minister, appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the monarch on the advice of the National Judicial Commission, a 4-member body to include the Legislative Committee of the National Assembly, the attorney general, the Chief Justice of Bhutan and the senior Associate Justice of the Supreme Court; other judges (drangpons) appointed by the monarch from among the High Court judges selected by the National Judicial Commission; chief justice serves a 5-year term or until reaching age 65 years, whichever is earlier; the 4 other judges serve 10-year terms or until age 65, whichever is earlier
subordinate courts: High Court (first appellate court); District or Dzongkhag Courts; sub-district or Dungkhag Courts
Political parties
Bhutan Tendrel Party or BTP
Druk Thuendrel Tshogpa or DTT
People's Democratic Party or PDP
United Party of Bhutan (Druk Nyamrup Tshogpa) or DNT
Diplomatic representation in the US
telephone: [1] (212) 682-2371
FAX: [1] (212) 661-0551
email address and website:
[email protected]
https://www.mfa.gov.bt/pmbny/
Diplomatic representation from the US
International organization participation
ADB, BIMSTEC, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Independence
17 December 1907 (became a unified kingdom under its first hereditary king); 8 August 1949 (Treaty of Friendship with India maintains Bhutanese independence)
National holiday
National Day (Ugyen WANGCHUCK became first hereditary king), 17 December (1907)
Flag
meaning: white stands for purity, and the jewels in the dragon's claws symbolize wealth; the background colors represent the spiritual and secular powers in Bhutan, with orange standing for Buddhism and yellow for the ruling dynasty
National symbol(s)
National color(s)
orange, yellow
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Gyaldun Dasho Thinley DORJI/Aku TONGMI
history: adopted 1953
Economy31
Economic overview
hydropower investments spurring economic development; Gross National Happiness economy; sharp poverty declines; low inflation; strong monetary and fiscal policies; stable currency; fairly resilient response to COVID-19; key economic and strategic relations with India; climate vulnerabilities
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $10.981 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2021: $10.437 billion (2021 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 5.2% (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2021: 4.4% (2021 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2022: $14,100 (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2021: $13,500 (2021 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$3.019 billion (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 4.2% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 5.6% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 29.6% (2023 est.)
services: 52.7% (2023 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
rice, milk, potatoes, root vegetables, maize, oranges, areca nuts, chillies/peppers, pumpkins/squash, carrots/turnips (2023)
Industries
cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages, calcium carbide, tourism
Industrial production growth rate
0% (2023 est.)
Labor force
406,500 (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 3.2% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 6% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 11.2% (2024 est.)
female: 16.5% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
12.4% (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 22.7% (2022 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2022: 3.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
Remittances 2021: 2.6% of GDP (2021 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $802.177 million (2020 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
12.3% (of GDP) (2020 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: -$963.122 million (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: -$805.723 million (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $867.871 million (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $791.342 million (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
India 92%, Italy 4%, Indonesia 1%, China 1%, Singapore 0% (2023)
Exports - commodities
iron alloys, aircraft, dolomite, semi-finished iron, cement (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $1.77 billion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $1.581 billion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
India 82%, Singapore 8%, China 5%, Thailand 2%, Indonesia 1% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, gold, plastics, broadcasting equipment, iron reductions (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $654.481 million (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $825.755 million (2022 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy6
Electricity access
Electricity
consumption: 11.914 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 6 billion kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 834.7 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 86.681 million kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
Coal
consumption: 105,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 54 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 122,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 0 (2024 est.) no service
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 100 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned TV station established in 1999; cable TV service offers dozens of Indian and other international channels; first radio station, privately launched in 1973, is now state-owned; 5 private radio stations are currently broadcasting (2012)
Internet country code
.bt
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2023 est.)
Transportation3
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
A5
Airports
4 (2025)
Heliports
8 (2025)
Military & Security6
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs: Royal Bhutan Police (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimated 7-8,000 active Royal Bhutan Army (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Royal Bhutan Army is lightly armed; it has a small amount of heavy equipment, such as armored cars and helicopters, originating from the former Soviet Union, India, and Thailand (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; militia training is compulsory for men aged 20-25 over a 3-year period (2025)
Military deployments
180 Central African Republic (MINUSCA) (2025)
Military - note
the Army is responsible for external threats but also has some internal security functions such as conducting counterinsurgency operations, guarding forests, and providing security for prominent persons; Bhutan's closest security partner is India; under the 2007 India-Bhutan Friendship Treaty, both countries agreed to cooperate closely on issues relating to their national interests (2025)
