Antarctica
Population
N/A
Area
14.2 km²
GDP
N/A
GDP Per Capita
N/A
Background
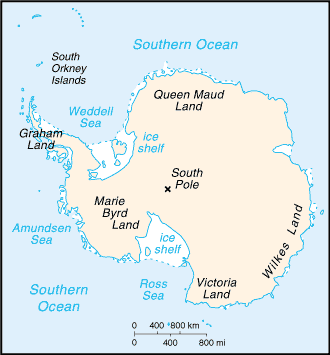
Geography15
Location
continent mostly south of the Antarctic Circle
Geographic coordinates
90 00 S, 0 00 E
Map references
Antarctic Region
Area
land: 14.2 million sq km (285,000 sq km ice-free, 13.915 million sq km ice-covered) (est.)
Area - comparative
slightly less than 1.5 times the size of the US
Land boundaries
Coastline
17,968 km
Maritime claims
Australia, Chile, and Argentina claim Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) rights or similar over 200 nm extensions seaward from their continental claims, but like the claims themselves, these zones are not accepted by other countries; 22 of 29 Antarctic Treaty consultative parties have made no claims to Antarctic territory, although Russia and the United States have reserved the right to do so, and no country can make a new claim
Climate
the coldest, windiest, and driest continent on Earth; severe low temperatures vary with latitude, elevation, and distance from the ocean; East Antarctica is colder than West Antarctica because of its higher elevation; Antarctic Peninsula has the most moderate climate; higher temperatures occur in January along the coast and average slightly below freezing; summers characterized by continuous daylight, while winters bring continuous darkness; persistent high pressure over the interior brings dry, subsiding air that results in very little cloud cover
Terrain
about 99% thick continental ice sheet and 1% barren rock, with average elevations between 2,000 and 4,000 m; mountain ranges up to nearly 5,000 m; ice-free coastal areas include parts of southern Victoria Land, Wilkes Land, the Antarctic Peninsula area, and parts of Ross Island on McMurdo Sound; glaciers form ice shelves along about half of the coastline, and floating ice shelves constitute 11% of the area of the continent
Elevation
lowest point: Denman Glacier more than -3,500 m (-11,500 ft) below sea level
mean elevation: 2,300 m
Natural resources
iron ore, chromium, copper, gold, nickel, platinum and other minerals, and coal and hydrocarbons have been found in small noncommercial quantities; mineral exploitation except for scientific research is banned by the Environmental Protocol to the Antarctic Treaty; krill, icefish, toothfish, and crab have been taken by commercial fisheries, which are managed through the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
Land use
Natural hazards
volcanism: volcanic activity on Deception Island and isolated areas of West Antarctica; other seismic activity rare and weak
Geography - note
mostly uninhabitable, 99% of the land area is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, the largest single mass of ice on Earth; it covers an area of 14 million sq km (5.4 million sq mi) and contains 26.5 million cu km (6.4 million cu mi) of ice (almost 62% of the world's fresh water)
People & Society1
Population
note: 56 countries have signed the 1959 Antarctic Treaty; 30 of those operate a number of seasonal-only (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent and its nearby islands; the population varies from approximately 5,000 in summer to 1,100 in winter, with about 1,000 support personnel on ships nearby
as of 2024, peak summer (December-February) maximum capacity in scientific stations - 4,713 total; Argentina 425, Australia 238, Belarus 15, Belgium 55, Brazil 64, Bulgaria 25, Chile 375, China 164, Czechia 32, Ecuador 35, Finland 16, France 136, France and Italy jointly 70, Germany 60, India 72, Italy 150, Japan 130, South Korea 158, New Zealand 85, Norway 60, Peru 30, Poland 41, Russia 211, South Africa 80, Spain 79, Sweden 16, Ukraine 15, United Kingdom 315, United States 1,495 , Uruguay 66 (2024)
winter (June-August) maximum capacity in scientific stations - 1,056 total; Argentina 221, Australia 52, Brazil 15, Chile 114, China 32, France 24, France and Italy jointly 13, Germany 9, India 48, Japan 40, Netherlands 10, South Korea 25, NZ 11, Norway 7, Poland 16, Russia 125, South Africa 15, Ukraine 12, UK 44, US 215, Uruguay 8 (2024)
Government4
Country name
conventional short form: Antarctica
etymology: name derived from two Greek words, anti and arktikos, meaning "opposite to the Arctic" or "opposite to the north"
Government type
decisions are made by consensus at annual meetings, and member countries implement these decisions through their national laws (see “Legal system”); additional agreements have strengthened the Treaty system, including conventions to protect seals (1972) and other marine life (1980), as well as an environmental protocol (1991, took effect in 1998); the protocol bans mining and includes strict rules on environmental impact, waste, pollution, wildlife, and protected areas; as of December 2024, there are 58 member nations: 29 consultative members, including the 7 claimant countries (Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the UK), and 29 non-consultative members; a permanent Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, established in 2004 in Buenos Aires, supports the system
Legal system
Flag
meaning: the bands represent the long days and nights at Antarctica's extreme latitude; the compass arrow is an homage to the continent's legacy of exploration; the peak and the arrow together create a diamond, symbolizing the hope that Antarctica will continue to be a center of peace, discovery, and cooperation
history: the flag is unofficial; created in 2018, the True South flag has quickly become popular for its simple yet elegant design and has been used by national Antarctic programs, Antarctic nonprofits, and expedition teams
Energy2
Coal
Petroleum
Communications2
Internet country code
.aq
Internet users
Transportation4
Airports
31 (2025)
Heliports
5 (2025)
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Transportation - note
US coastal stations include McMurdo (77 51 S, 166 40 E) and Palmer (64 43 S, 64 03 W); government use only; all ships are subject to inspection in accordance with Article 7 of the Antarctic Treaty; ships must comply with relevant legal instruments and authorization procedures under the Antarctic Treaty (see "Legal System"); The Hydrographic Commission on Antarctica (HCA), a commission of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), coordinates and facilitates provision of accurate and appropriate charts and other aids to navigation; membership in HCA is open to any IHO Member State whose government has acceded to the Antarctic Treaty and which contributes resources or data to IHO Chart coverage of the area
Military & Security1
Military - note
the Antarctic Treaty of 1961 prohibits any measures of a military nature, such as the establishment of military bases and fortifications, the carrying out of military maneuvers, or the testing of any type of weapon; it permits the use of military personnel or equipment for scientific research or for any other peaceful purposes
